2–10 EPM 6000 MULTI-FUNCTION POWER METERING SYSTEM – USER GUIDE
CHAPTER 2: ELECTRICAL BACKGROUND
As shown in the above table, the accumulated energy for the power load profile of the
data in Power Use Over Time on page 2–9 is 14.92 kWh.
2.3.4 Demand
Demand is also a time-based value. The demand is the average rate of energy use over
time. The actual label for demand is kilowatt-hours/hour but this is normally reduced to
kilowatts. This makes it easy to confuse demand with power. But demand is not an
instantaneous value. To calculate demand it is necessary to accumulate the energy
readings (as illustrated in Power Use Over Time on page 2–9) and adjust the energy reading
to an hourly value that constitutes the demand.
In the example, the accumulated energy is 14.92 kWh. But this measurement was made
over a 15-minute interval. To convert the reading to a demand value, it must be
normalized to a 60-minute interval. If the pattern were repeated for an additional three 15-
minute intervals the total energy would be four times the measured value or 59.68 kWh.
The same process is applied to calculate the 15-minute demand value. The demand value
associated with the example load is 59.68 kWh/hour or 59.68 kWd. Note that the peak
instantaneous value of power is 80 kW, significantly more than the demand value.
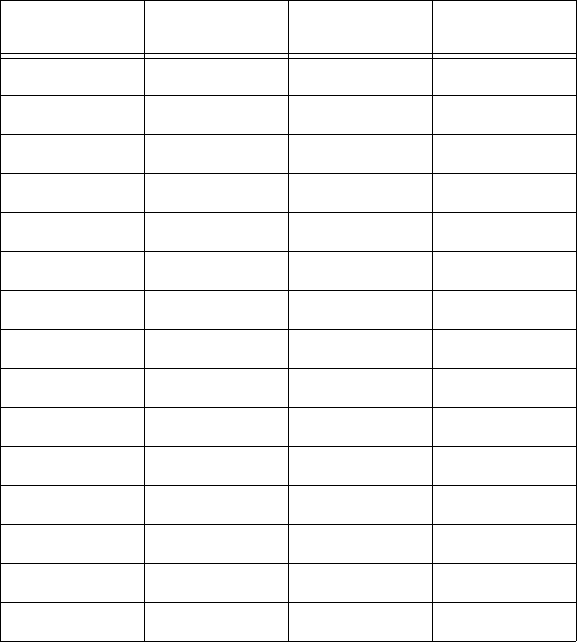
Table 2–2: Power and Energy Relationship Over Time
Time Interval Power Energy Accumulated
Energy
1 minute 30 kW 0.50 kWh 0.50 kWh
2 minutes 50 kW 0.83 kWh 1.33 kWh
3 minutes 40 kW 0.67 kWh 2.00 kWh
4 minutes 55 kW 0.92 kWh 2.92 kWh
5 minutes 60 kW 1.00 kWh 3.92 kWh
6 minutes 60 kW 1.00 kWh 4.92 kWh
7 minutes 70 kW 1.17 kWh 6.09 kWh
8 minutes 70 kW 1.17 kWh 7.26 kWh
9 minutes 60 kW 1.00 kWh 8.26 kWh
10 minutes 70 kW 1.17 kWh 9.43 kWh
11 minutes 80 kW 1.33 kWh 10.76 kWh
12 minutes 50 kW 0.83 kWh 12.42 kWh
13 minutes 50 kW 0.83 kWh 12.42 kWh
14 minutes 70 kW 1.17 kWh 13.59 kWh
15 minutes 80 kW 1.33 kWh 14.92 kWh