3 - 14
3 Function Specifications
MITSUBISHI CNC
3-3-6 Lost motion compensation type 2
Servo motor always drives the machine opposing to the frictional force, and the torque which is required to
oppose the friction during the axis movement is outputted by I control (Integral control) of the speed loop PI
control. When the movement direction is changed, the frictional force works in the opposite direction
momentarily, however, the machine will stop while the command torque is less than the frictional force as it
takes some time to reverse the command torque in I control.
When the movement direction is changed, the frictional force works in the opposite direction momentarily,
however, the machine will stop while the command torque is less than the frictional force as it takes some
time to reverse the command torque in I control.
With the this lost motion compensation function improves the accuracy worsened by the stick motion.
3-3-7 Lost motion compensation type 3
For a machine model where the travel direction is reversed, the compensation in accordance with the
changes in the cutting conditions is enabled by also considering the spring component and viscosity
component in addition to the friction.
This function can be used to accommodate quadrant projection changes that accompany feed rate and
circular radius changes which could not be compensated by Lost motion compensation type 2.
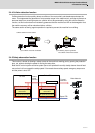
1.Mechanical spring elements can't be ignored.
2.Changes between static and dynamic frictions are
wide and steep.
Not only frictions but spring element and viscosity element can
be compensated, thus quadrant protrusions are suppressed
within a wide band.
Conventional control can’t perform enough compensation.
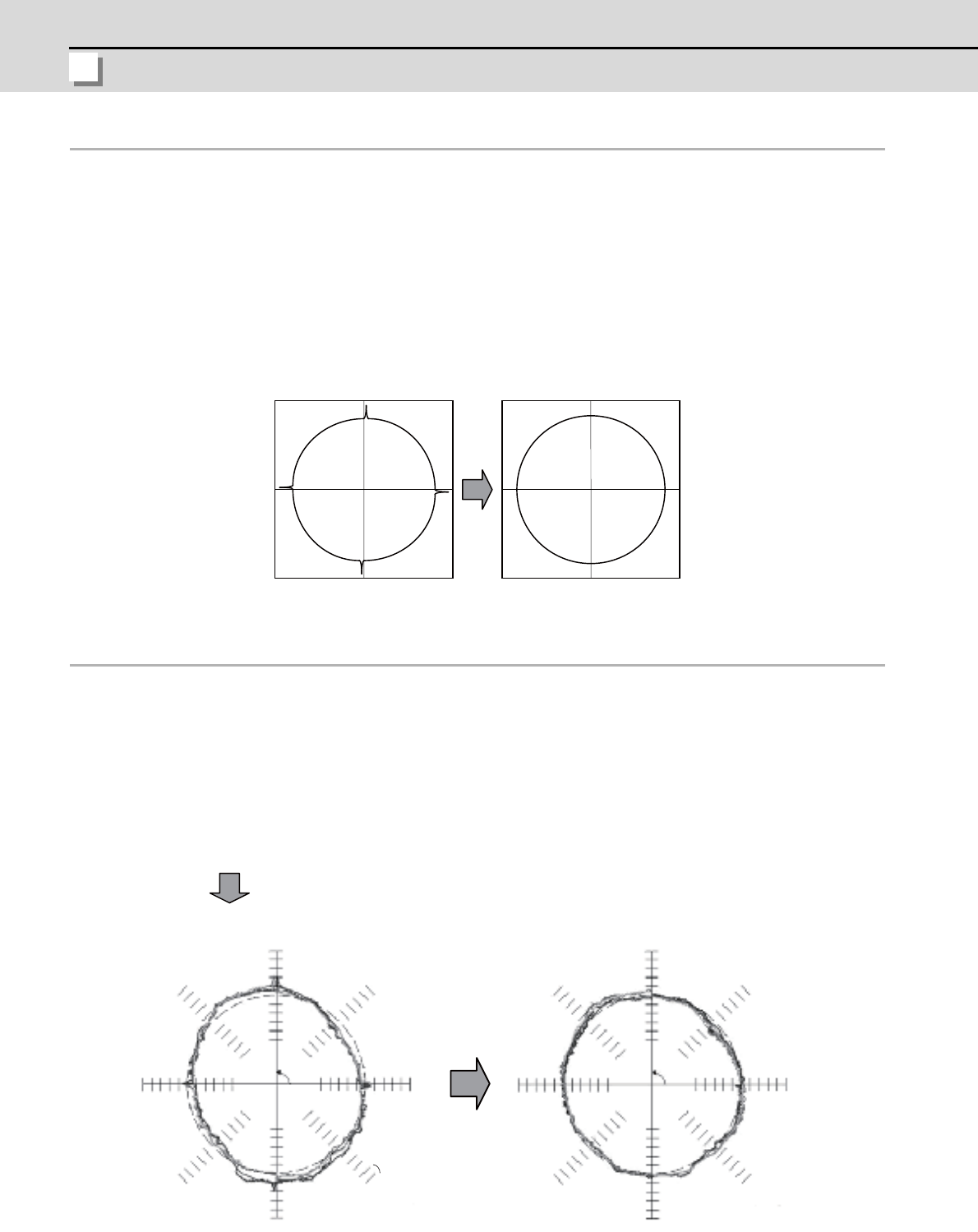
Conventional compensation control Lost motion compensation control type 3
No compensation With compensation
+Y
+Y
+X
+X
3μm