5-2
Power and Grounding Requirements
411-2021-111 Standard 01.01 June 1996
Power and grounding requirements
Typical cell site radio equipment is powered by a +24 Vdc power system.
However, the primary power for a DualMode Metrocell is +27 Vdc nominal.
The reason that +27 Volts is specified as the nominal voltage rather than +24
Volts is to highlight that the system requires the full float voltage level to
enable it to deliver its fully rated available transmit RF output power level.
When AC power is lost and the voltage level to the system is reduced to the
nominal battery (that is, +24 Vdc), the power amplifiers will automatically
step down their transmit RF output power. See the Dual Power Amplifier
(DPA) section in NTP 411-2021-113
Metrocell Radio Frequency (RF) Frame
Description
for details.
The power plant normally consists of a negative grounded 12-cell Valve
Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) battery plant and AC powered battery charging
units commonly referred to as the rectifiers. Under normal operating
conditions, that is, when AC power is available, the batteries are maintained
within their specified float voltage range via the rectifiers which must supply
current to power the system and keep the batteries charged. When an AC
outage occurs, the battery plant provides back-up power to the system.
However, at this time, the system will experience a step drop in voltage due to
a battery plant transition from the float state to the fully charged state. During
the battery discharge period, the voltage supplied to the system will gradually
drop from its fully charged voltage.
Under normal operating conditions an equalizing charge is not required. An
equalizing charge is a special charge given to a battery when non-uniformity
in voltage has developed between cells. It is given to restore all units to a
fully charged condition by using a charging voltage higher than the normal
float voltage and for a specified number of hours as determined by the specific
voltage used. An equalize charge is also often applied when a recharge of the
batteries is required in a minimum time following an emergency discharge.
A typical operating voltage range at the Power Distribution Plant of a
Metrocell should not exceed the range between +22.8 Vdc to +29 Vdc. +22.8
Vdc assumes 1 V drop from the batteries to the Rack Interface Panel (RIP)
and 0.8 V from the RIP to the load. The operating voltage range of a specific
system could vary.
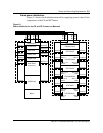
The power plant supplies two (designated as ‘A’ and ‘B’) power feeds to each
Metrocell frame. Table 5-1 lists the performance requirements related to
primary DC power in a Metrocell.