Prestige 792H G.SHDSL Router
8-6 Firewalls
2-b In a LAND Attack, hackers flood SYN packets into the network with a spoofed source IP
address of the targeted system. This makes it appear as if the host computer sent the packets to
itself, making the system unavailable while the target system tries to respond to itself.
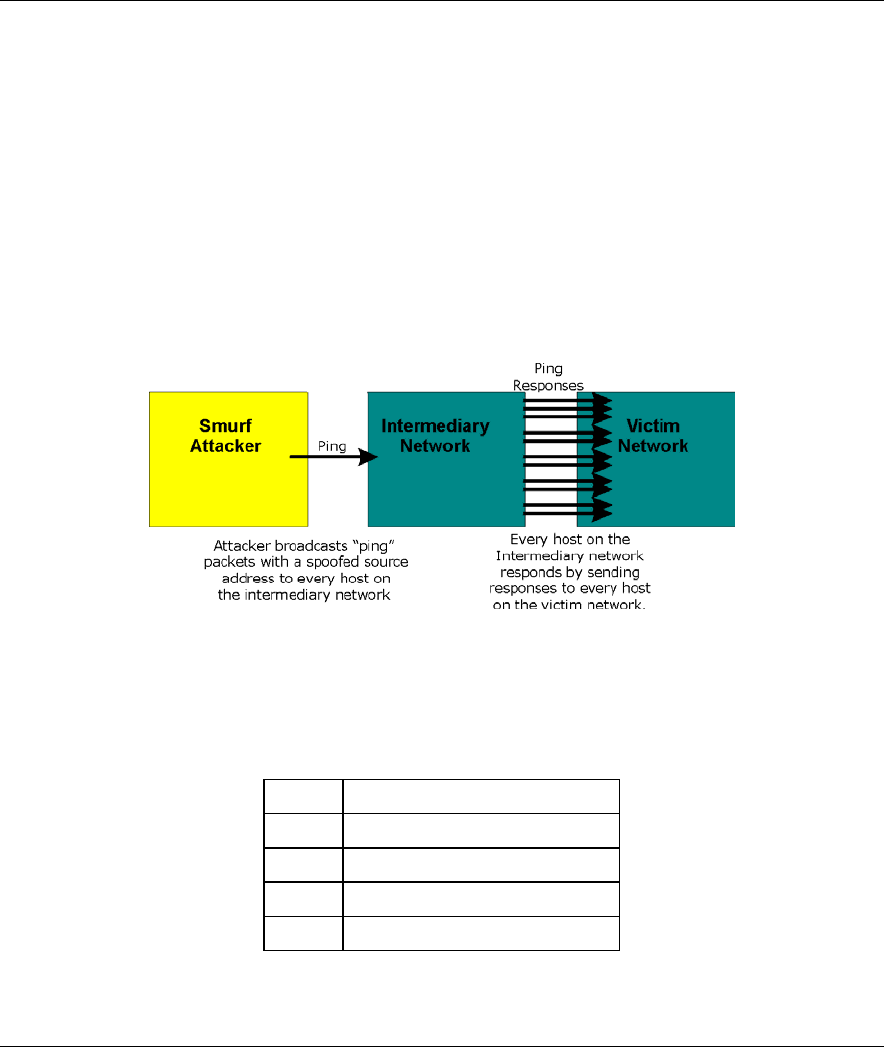
3. A brute-force attack, such as a "Smurf" attack, targets a feature in the IP specification known as
directed or subnet broadcasting, to quickly flood the target network with useless data. A Smurf hacker
floods a router with Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo request packets (pings). Since the
destination IP address of each packet is the broadcast address of the network, the router will broadcast
the ICMP echo request packet to all hosts on the network. If there are numerous hosts, this will create a
large amount of ICMP echo request and response traffic. If a hacker chooses to spoof the source IP
address of the ICMP echo request packet, the resulting ICMP traffic will not only clog up the
"intermediary" network, but will also congest the network of the spoofed source IP address, known as
the "victim" network. This flood of broadcast traffic consumes all available bandwidth, making
communications impossible.
Figure 8-4 Smurf Attack
ICMP Vulnerability
ICMP is an error-reporting protocol that works in concert with IP. The following ICMP types trigger an alert:
Table 8-2 ICMP Commands That Trigger Alerts
5 REDIRECT
13 TIMESTAMP_REQUEST
14 TIMESTAMP_REPLY
17 ADDRESS_MASK_REQUEST
18 ADDRESS_MASK_REPLY
Illegal Commands (NetBIOS and SMTP)


















