3-15
Cisco ASR 903 Router Hardware Installation Guide
OL-25178-04
Chapter 3 Installing the Cisco ASR 903 Router
Interface Module Installation
Caution Do not use interface module and power supply ejector handles to lift the chassis; using the handles to
lift the chassis can deform or damage the handles.
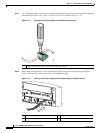
Removing an Interface Module
Step 1 To remove an interface module, disconnect all the cables from each interface module.
Step 2 Loosen the locking thumbscrews on both sides of the interface module.
Step 3 Slide the interface module out of the router slot by pulling on the handles. If you are removing a blank
filler plate, pull the blank filler plate completely out of the router slot using the captive screws.
Hot-Swapping an Interface Module
The Cisco ASR 903 Router provides a feature that allows you to remove and replace an interface module
without powering down the router. This feature, called hot-swapping or OIR, allows you to remove and
replace a redundant module without disrupting router operation.
Note The Cisco ASR 903 Router does not support hot-swapping an interface module with another module of
a different type. For example, you cannot swap an SFP Gigabit Ethernet module with a copper Gigabit
Ethernet module without disrupting router operation.
Note If you perform OIR on an interface module and move the module to a different slot, the router does not
retain the module configuration; you must reconfigure the interface module.
When you remove or insert a redundant module while the router is powered on and running, the router
does the following:
1. Determines if there is sufficient power for the module.
2. Scans the backplane for configuration changes.
3. Initializes the newly inserted module. In addition, the system notes any removed modules and places
those modules in the administratively shutdown state.
4. Places any previously configured interfaces on the module back to the state they were in when they
were removed.
The router runs diagnostic tests on any new interfaces and the test results indicate the following:
• If the tests pass, the router is operating normally.
• If the new module is faulty, the router resumes normal operation but leaves the new interfaces
disabled.
• If the diagnostic tests fail, the router stops operating, which usually indicates that the new module
has a problem in the bus and should be removed.