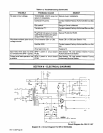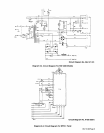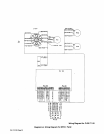
9-4.
PLUG
WELDS
Plug
welds
provide
a
means
of
joining
two
pieces
of
metal
where
the
thickness
of
the
top
sheet
is
beyond
the
normal
range
of
the
welding
power
source
or
where
sheet
metal
sections
are
too
thin
to
be
spot
welded
or
pulsed
welded
without
producing
distortion
or
burn
throughs.
The
plug
weld
is
made
by
drilling
or
punching
a
hole
in
the
top
sheet,
clamping
the
metal
sections
tightly
together,
and
filling
the
hole
with
a
weldment.
The
plug
weld
can
be
timed
using
the
spot
timer
or
untimed.
Plug
welds
should
be
spaced
1
to
1-1/2
inches
(25-38
mm)
apart.
Plug
welds
on
sample
materials
should
be
made
so
that
proper
parameters
can
be
set.
9-5.
SKIP
WELDING
Skip
welding
provides
a
means
of
making
a
series
of
short
welds,
usually
less
than
3/4
in.,
(18
mm)
in
length
each,
consistent
in
size
and
appearance.
Skip
welding
can
be
accomplished
with
this
unit
by
setting
a
spot
weld
time
and
jogging
the
gun
trigger
off
and
on
again
each
time
the
spot
timer
times
out.
Skip
welds
on
sample
material
should
be
made
so
that
proper
parameters
can
be
set.
9-6.
TROUBLESHOOTING
THE
GAS
METAL
ARC
WELDING
PROCESS
A.
Porosity
Figure
9-9.
Porosity
Remove
spatter
from
the
gun
nozzle.
Check
gas
hoses
for
leaks.
Eliminate
drafts
(from
fans,
open
doors,
etc.)
blowing
into
the
welding
arc.
Place
nozzle
1/4
to
5/16
in.
(6-8
mm)
from
workpiece.
Increase
gas
flow
to
displace
all
air
from
the
weld
zone.
Decrease
excessive
gas
flow
to
avoid
turbulence
and
the
en
trapment
of
air
in
the
weld
zone.
Hold
gun
at
end
of
weld
until
molten
metal
solidifies.
Check
for
frozen
C02
regulator/flowmeter.
2.
Wrong
gas.
Use
welding
grade
shielding
gas.
3.
Dirty
welding
wire.
Use
clean
and
dry
welding
wire.
Eliminate
pick
up
of
oil
or
lubricant
on
welding
wire
from
feeder
or
conduit.
4.
Workpiece
dirty.
Remove
all
grease,
oil,
moisture,
rust,
paint,
undercoating,
and
dirt
from
work
surface
before
welding.
Use
a
more
highly
deoxidizing
welding
wire.
5.
Welding
wire
extends
too
far
out
of
nozzle.
Welding
wire
should
extend
1/4
in.
(6
mm)
out
of
nozzle.
Possible
Causes
1.
Inadequate
shielding
gas
coverage.
Corrective
Actions
OM-113
336
Page
37