2.3 Other wiring
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
28
2.3 Other wiring
2.3.1 Power harmonics
Power harmonics may be generated from the converter section of the inverter, affecting power supply
equipment, power capacitors, etc. Power harmonics are different in generation source, frequency and
transmission path from radio frequency (RF) noise and leakage currents. Take the following counter
measures.
•
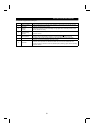
The differences between harmonics and RF noise are indicated below:
Item Harmonics RF Noise
Frequency
Normally 40th to 50th degrees or less, (up
to 3kHz or less)
High frequency (several 10kHz to MHz order)
Environment To wire paths, power impedance Across spaces, distance, laying paths
Quantitative understanding Logical computation is possible Occurs randomly, quantitative understanding is difficult.
Generated amount Approximately proportional to load capacity
According to current fluctuation rate (larger with faster
switching)
Immunity of affected device Specified in standards for each device. Differs according to maker’s device specifications.
Example of safeguard Install a reactor Increase the distance.
•
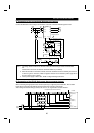
Safeguard
The harmonic current generated from the inverter to the
power supply differs according to various conditions such
as the wiring impedance, whether a power factor
improving reactor is used or not, and output frequency
and output current on the load side.
For the output frequency and output current, the
adequate method is to obtain them under rated load at
the maximum operating frequency.
NFB
IM
Inverter
Power factor
improving DC
reactor
Moto
r
Do not insert power factor
improving capacitor
Power factor
improving AC
reactor
Note: A power factor improving capacitor or surge suppressor on the inverter’s output may overheat or be
damaged due to the harmonics of the inverter output. Also, since the overcurrent protection is activated by
an overcurrent that flows in the inverter, do not insert a capacitor or surge suppressor on the inverter's
output when the motor is inverter-driven. To improve the power factor, insert a power factor improving
reactor in the inverter’s input or DC circuit. For details, refer to the technical information.
2