Component Descriptions
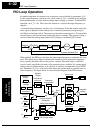
Motor Control
Accessories
5–4
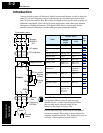
Zero-phase Reactor (RF Noise Filter)
The zero-phase reactor helps reduce
radiated noise from the inverter wiring. It
can be used on the input or output side of
the inverter. The example zero-phase
reactor shown to the right comes with a
mounting bracket. The wiring must go
through the opening to reduce the RF
component of the electrical noise. Loop
the wires three times (four turns) to attain
the full RF filtering effect. For larger wire
sizes, place multiple zero-phase reactors
(up to four) side-by-side for a greater
filtering effect.
EMI Filter
The EMI filter reduces the conducted noise on the power supply wiring generated by the
inverter. Connect the EMI filter to the inverter primary (input side). The FFL100 series
filter is required for compliance to the EMC Class A directive (Europe) and C-TICK
(Australia). See “
CE–EMC Installation Guidelines” on page C–2.
WARNING: The EMI filter has high internal leakage current from power wiring to the
chassis. Therefore, connect the chassis ground of the EMI filter before making the power
connections to avoid danger of shock or injury.
RF Noise Filter (Capacitive)
This capacitive filter reduces radiated noise from the main power wires in the inverter
input side. This filter is not for achieving CE compliance and is applicable to the input
side only of the inverter. It comes in two versions—for 200V class inverters or 400V
class inverters. Please refer to the documentation that comes with the radio noise filter
for installation instructions.
DC Link Choke
The DC choke (reactor) suppresses harmonics generated by the inverter. It attenuates the
high-frequency components on the inverter’s internal DC bus (link). However, note that
it does not protect the diode rectifiers in the inverter input circuit.
ZCL–xxx
FFL100–xxx