3 Operating the Power Supply Locally
44 Series N5700 User’s Guide
• Set the programming sources to the desired levels and turn
the power supply on. Adjust the programming sources to
change the power supply output.
The analog control circuits let you set the output voltage and current
limit up to 5% over the model-rated maximum value. The power
supply will operate within the extended range, however it is not
recommended to operate the power supply over its voltage and
current rating, and performance in this region is not guaranteed.
SW1 switch 3 Voltage Programming
(J1 pin 9)
Current Programming
(J1 pin 10)
Down (default) 0 – 5 V 0 – 5 V
Up 0 – 10 V 0 – 10 V
Resistance Programming of Output Voltage and Current
Resistances of 0 - 5 kΩ or 0 - 10 kΩ can be selected to program the
output voltage and current limit from zero to full scale. Internal
current sources supply a 1mA current through the external resistors.
The voltage drop across the resistors is used as the programming
voltage for the power supply. To maintain the temperature stability
specification of the power supply, only use resistors that are stable
and low noise, with a temperature coefficient less than 50ppm.
Set the power supply to resistance programming as follows:
• Make sure that the power supply is turned off.
• Set SW1 setup switch 1 (for voltage) and 2 (for current) to
the UP position.
• Set SW1 setup switch 3 to select programming resistance
range according to the following table.
• Set SW1 setup switch 7 (for voltage) and 8 (for current) to
the Up position to enable resistance programming.
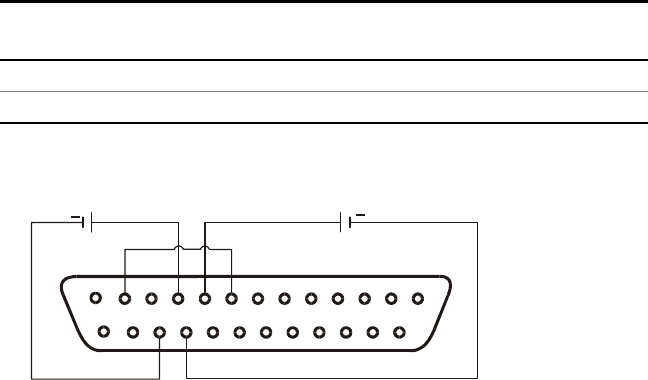
• Connect a short between J1 pin 8 and J1 pin 12 (see figure).
• Connect the programming resistors to the mating plug of J1
as shown in the following figure. A variable resistor can
control the output over its entire range, or a combination of
variable resistor and series/parallel resistors can control the
output over a restricted portion of its range.
1
14
13
25
10
12
8
9
23
22
+
+
CURRENT LIMIT
PROGRAMMING
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
PROGRAMMING


















