Measurement of main circuit voltages, currents and powers
96
PRECAUTIONS FOR MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
5.2.7 Measurement of inverter output frequency
In the initial setting of the FM-type inverter, a pulse train proportional to the output frequency is output across the pulse train
output terminals FM and SD of the inverter. This pulse train output can be counted by a frequency counter, or a meter
(moving-coil type voltmeter) can be used to read the mean value of the pulse train output voltage. When a meter is used to
measure the output frequency, approximately 5 VDC is indicated at the maximum frequency.
For detailed specifications of the pulse train output terminal FM, refer to the FR-A800 Instruction Manual (Detailed).
In the initial setting of the CA-type inverter, a pulse train proportional to the output frequency is output across the analog
current output terminals CA and 5 of the inverter. Measure the current using an ammeter or tester.
For detailed specifications of the analog current output terminal CA, refer to the FR-A800 Instruction Manual (Detailed).
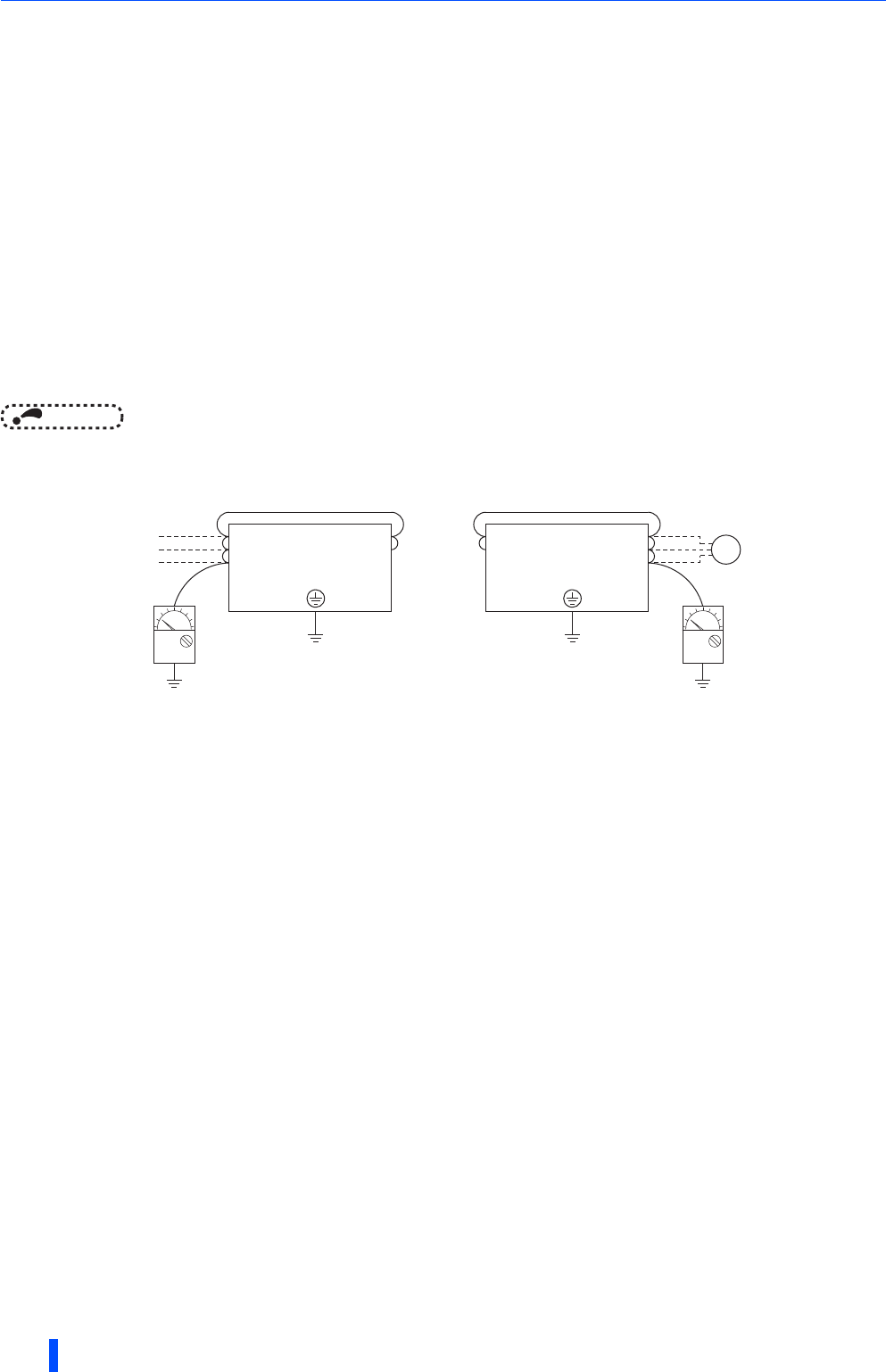
5.2.8 Insulation resistance test using megger
• For the inverter and the converter unit (FR-CC2), conduct the insulation resistance test on the main circuit only as shown
below and do not perform the test on the control circuit. (Use a 500 VDC megger.)
NOTE
• Before performing the insulation resistance test on the external circuit, disconnect the cables from all terminals of the inverter
and the converter unit so that the test voltage is not applied to the inverter and the converter unit.
• For the continuity test of the control circuit, use a tester (high resistance range) and do not use the megger or buzzer.
5.2.9 Pressure test
Do not conduct a pressure test. Deterioration may occur.
500VDC
megger
Power
supply
Motor
P/+
N/-
Converter
unit
U
V
W
Inverter
IM
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
P/+
N/-
Earth (ground) terminal Earth (ground) terminal
500VDC
megger


















