1-2
Cisco ASA 5500-X Series Hardware Installation Guide
Chapter 1 Information about the ASA 5500-X
Cisco ASA 5500-X Series Chassis Overview
Cisco ASA 5500-X Series Chassis Overview
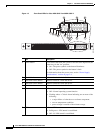
This guide supports the Cisco ASA 5500-X series models, which includes the ASA 5512-X,
ASA 5515-X, ASA 5525-X, ASA 5545-X, and ASA 5555-X.
The Cisco ASA 5500-X series is a family of next-generation mid-range ASAs that are built on the same
security platform as the rest of the ASA family. These next-generation ASAs provide more firewall
throughput (4X firewall throughput), better scaling, more Ethernet ports (up to 14 GE ports), optional
ASA CX SSP or ASA IPS SSP software modules, and redundant power supplies on the 5545-X and
5555-X models.
For More Information
• For information about ASA 5500-X performance, see the “Hardware Specifications” section on
page 1-15.
• For information about ASA IPS functionality, see Cisco Intrusion Prevention System
documentation:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/vpndevc/ps4077/products_documentation_roadmaps_lis
t.html
• For information about ASA CX functionality, see:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/security/asacx/roadmap/asacxprsmroadmap.html
Internal and External USB Flash Drives
The Cisco ASA 5500-X series chassis have internal and (optional) external USB drives.
• Internal USB Drive, page 1-2
• (Optional) External USB Drives, page 1-2
• Online Insertion and Removal Support, page 1-3
• FAT 32 File System, page 1-3
Internal USB Drive
An embedded USB (eUSB) device is used as the internal flash (disk0). See the “Hardware
Specifications” section on page 1-15 for the size shipped with each model.
(Optional) External USB Drives
The ASA 5500-X series supports external USB flash drives for data storage. The ASA 5500-X series use
disk1 as the external USB flash drive identifier. When the ASA is powered on, an inserted USB flash
drive is mounted to disk1 and available for you to use. Additionally, the file system commands that are
available to disk0 are also available to disk1, including copy, format, delete, mkdir, pwd, cd, and so
on. When you remove the USB flash drive, the system unmounts disk1, and disk1 becomes an invalid
file system label that you can no longer access.
If you insert a USB drive with more than one partition, only the first partition is mounted.