Prosine 2.5/3.0 Installation & Operation Guide 77
Section 7: Batteries
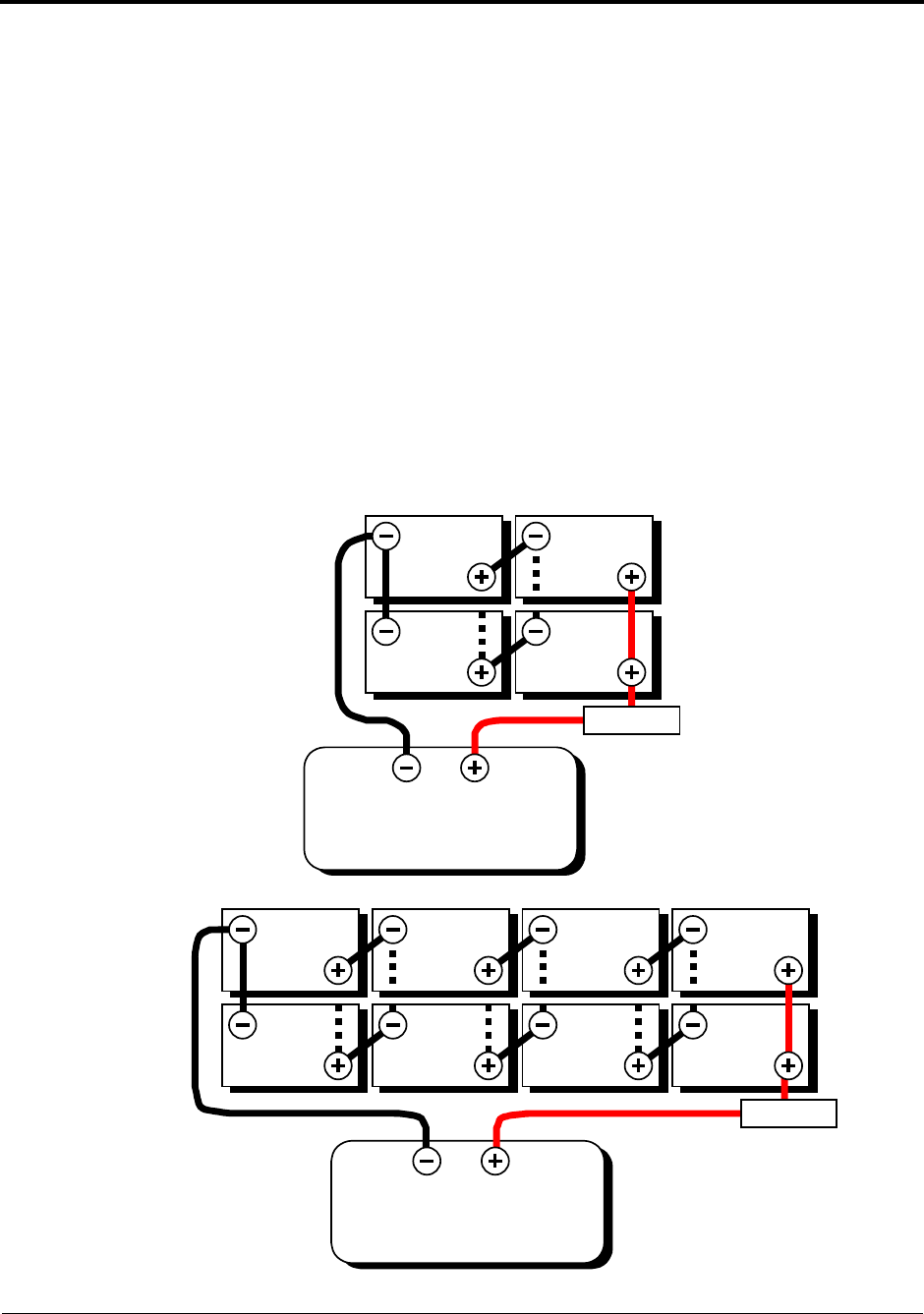
Series – Parallel Connection
As the name implies, both the series and parallel techniques are used in combination. The result is an
increase in both the voltage and the capacity of the total battery bank. This is done very often to make
a larger, higher voltage battery bank out of several smaller, lower voltage batteries. This is common
with all battery-inverter system voltages. The smaller, lower voltage batteries are first connected in
series to obtain the needed voltage, and then these “batteries, connected in series” sets are connected
in parallel to increase the battery bank capacity.
The best arrangement when using a series-parallel configuration is to connect all the smaller, lower
voltage batteries in parallel, then connect all these “batteries in parallel” into series sets to obtain the
needed voltage. This configuration is often called “cross-tying.” This is less convenient and requires
additional cables but reduces imbalances in the battery, can improve the overall performance.
Cross-tying (shown as dashed -------- lines in the illustration below) helps equalize the voltage in the
batteries. If cross-tying is not desired, the dash lines can be ignored.
12V INVERTER
(Total Battery Capacity
= 200 Amp Hours)
6V 6V
6V 6V
FUSED
DISCONNECT
6V 6V
24V INVERTER
(Total Battery Capacity
= 200 Amp Hours)
6V 6V
FUSED
DISCONNECT
6V 6V 6V 6V
100 Ah
100 Ah
100 Ah 100 Ah
100 Ah 100 Ah
100 Ah 100 Ah
100 Ah
100 Ah
100 Ah
100 Ah
24V
12V