12-6
Cisco IOS Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points
OL-11350-01
Chapter 12 Configuring WDS, Fast Secure Roaming, Radio Management, and Wireless Intrusion Detection
Understanding Wireless Intrusion Detection Services
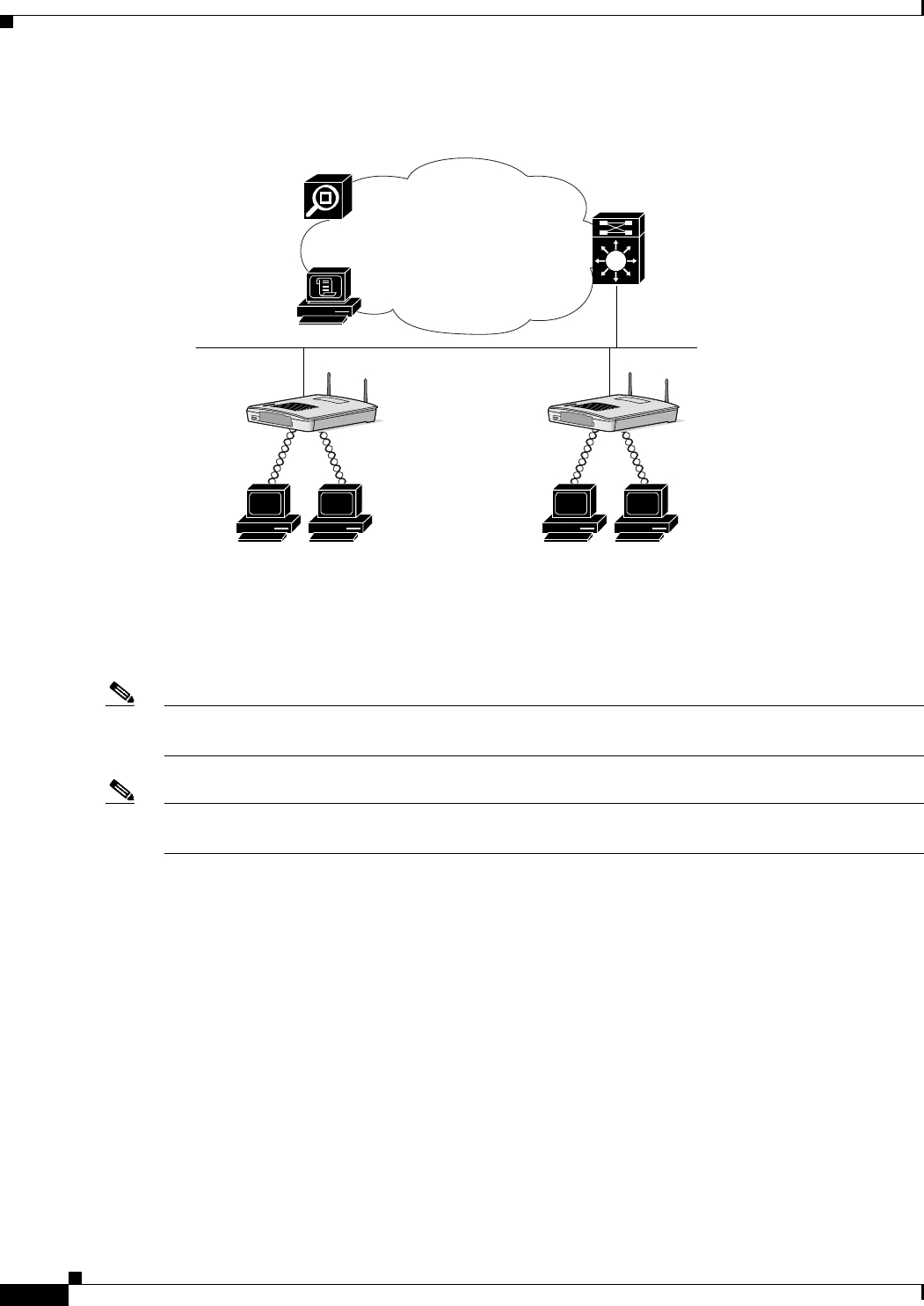
Figure 12-3 Required Components for Layer 3 Mobility
Click this link to browse to the information pages for the Cisco Structured Wireless-Aware Network
(SWAN):
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/netsol/ns340/networking_solutions_large_enterprise_home.html
Note If you enable Layer 3 mobility for an SSID and your WDS device does not support Layer 3 mobility,
client devices cannot associate using that SSID.
Note Repeater access points and access points in workgroup bridge mode cannot associate to an SSID on
which Layer 3 mobility is enabled.
Understanding Wireless Intrusion Detection Services
When you implement Wireless Intrusion Detection Services (WIDS) on your wireless LAN, your access
points, WLSE, and an optional (non-Cisco) WIDS engine work together to detect and prevent attacks on
your wireless LAN infrastructure and associated client devices.
Working with the WLSE, access points can detect intrusions and take action to defend the wireless LAN.
WIDS consists of these features:
• Switch port tracing and rogue suppression—Switch port tracing and suppression uses an RF
detection method that produces the radio MAC address of an unknown radio (a potential rogue
device). The WLSE derives a wired-side MAC address from the wireless MAC address and uses it
to search the switch’s BRIDGE MIB. When one or more searchable MAC addresses are available,
the WLSE uses CDP to discover any switches connected up to two hops away from the detecting
CiscoWorks Wireless LAN Solution Engine
(WLSE)
CiscoSecure ACS
AAA Server
Catalyst 6500
Wireless Domain Services (WDS) on the
Wireless LAN Solutions Module (WLSM)
Catalyst 6500
Wireless Domain Services (WDS) on the
Wireless LAN Solutions Module (WLSM)
Infrastructure access points
(registered with WDS)
117993


















