Spanning Tree
ROS™ v3.5 134 RS400
• RSTP offers edge port recognition, allowing ports at the edge of the network to forward
frames immediately after activation while at the same time protecting them against loops.
While providing much better performance than STP, IEEE 802.1w RSTP still required up to
several seconds to restore network connectivity when a topology change occurred.
A revised and highly optimized RSTP version was defined in the IEEE standard 802.1D-2004
edition. IEEE 802.1D-2004 RSTP reduces network recovery times to just milliseconds and
optimizes RSTP operation for various scenarios.
ROS
TM
supports IEEE 802.1D-2004 RSTP.
5.1.1 RSTP States and Roles
RSTP bridges have roles to play, either root or designated. One bridge, the root bridge, is the
logical center of the network. All other bridges in the network are designated bridges.
RSTP also assigns each port of the bridge a state and a role. The RSTP state describes what is
happening at the port in relation to address learning and frame forwarding. The RSTP role
basically describes whether the port is facing the center or the edges of the network and
whether it can currently be used.
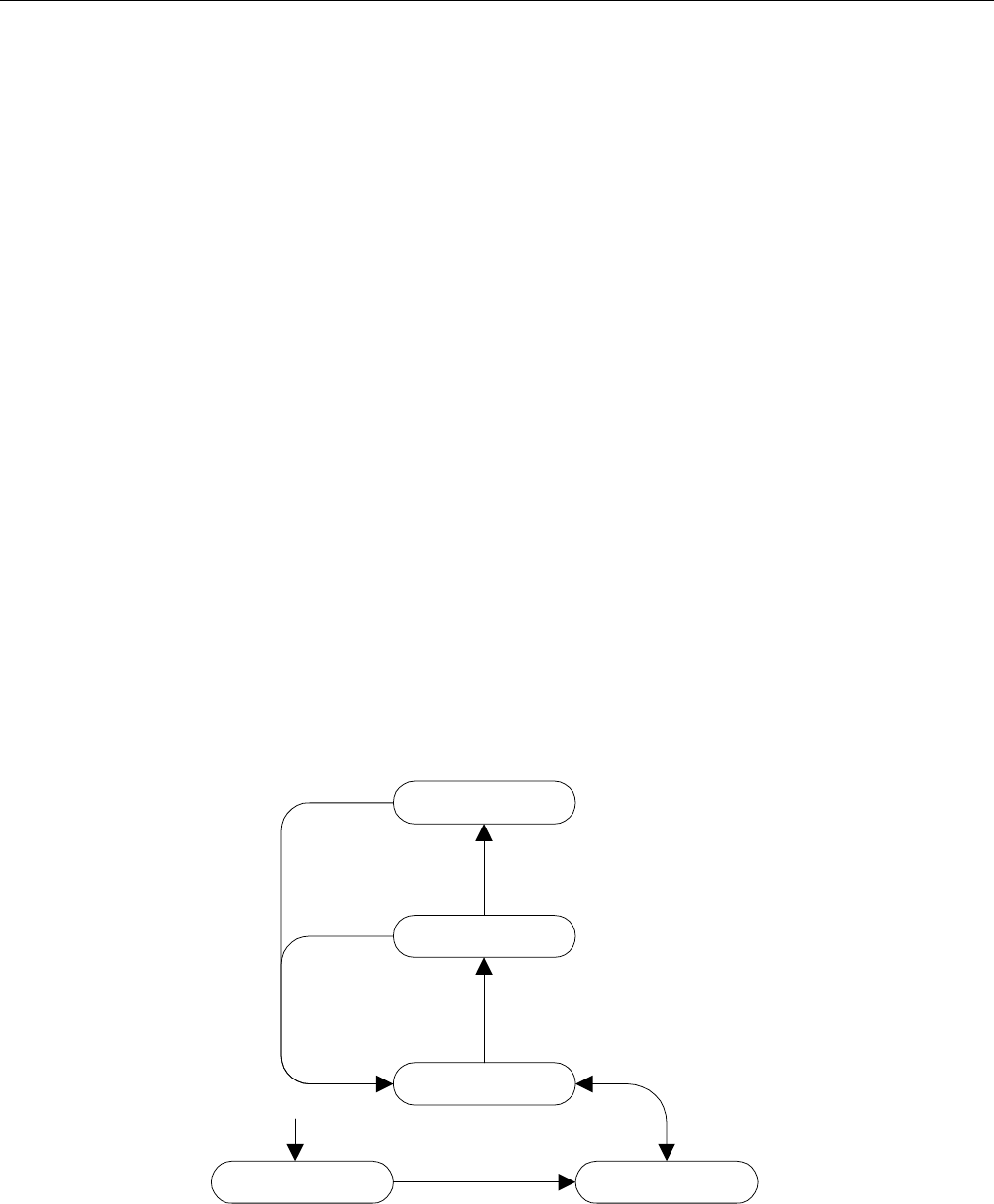
State
There are three RSTP states: Discarding, Learning and Forwarding.
The discarding state is entered when the port is first put into service. The port does not learn
addresses in this state and does not participate in frame transfer. The port looks for RSTP traffic
in order to determine its role in the network. When it is determined that the port will play an
active part in the network, the state will change to learning.
Forwarding
Learning
Discarding
Disabled Link Down
Forwarding Timer Expires
Or Active RSTP Handshake
Forwarding Timer Expires
Or Active RSTP Handshake has
Occurred
Link rises or falls
RSTP Enabled
BPDUS indicate
port should not
be active
RSTP Disabled in any state
Figure 94: Bridge and Port States


















