Spanning Tree
RS400 143 ROS™ v3.5
5.3 RSTP Applications
5.3.1 RSTP in Structured Wiring Configurations
RSTP allows you to construct structured wiring systems in which connectivity is maintained in
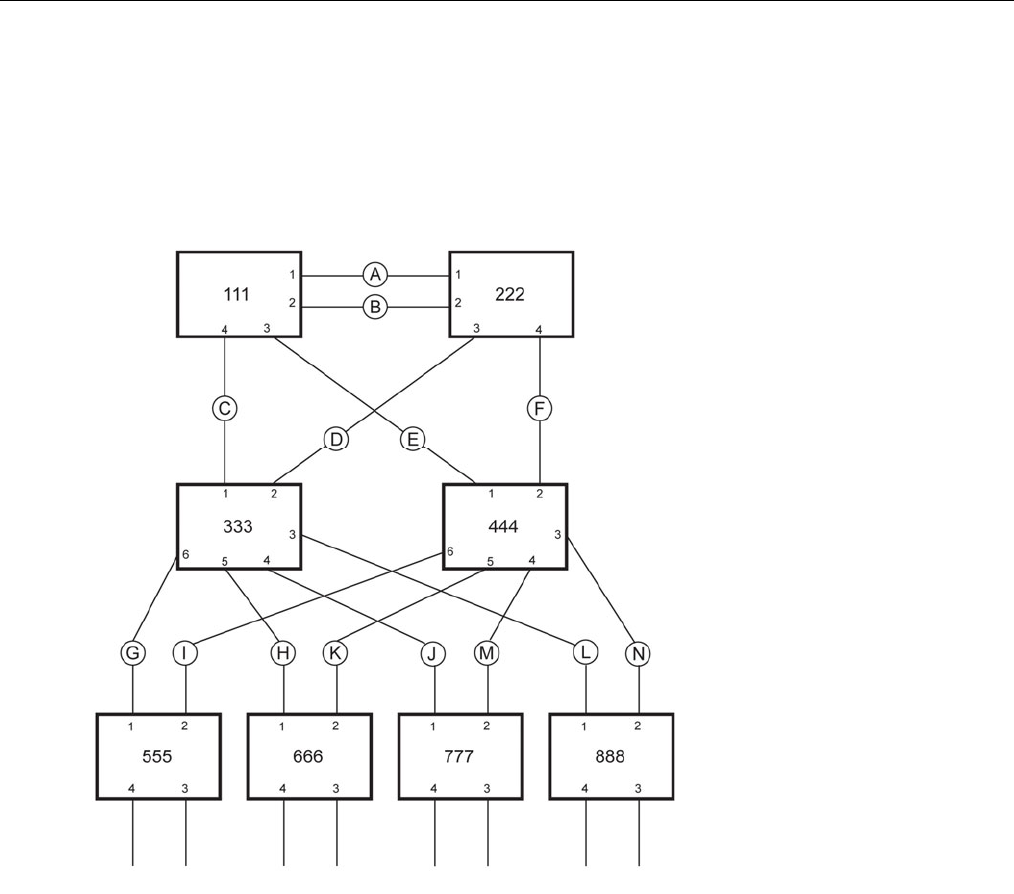
the event of link failures. For example a single link failure of any of links A through N in Figure
96 would leave all the ports of bridges 555 through 888 connected to the network.
Figure 96: Example of a Structured Wiring Configuration
Design Considerations for RSTP in Structured Wiring Configurations
1. Select the design parameters for the network.
What are the requirements for robustness and network failover/recovery times? Are there
special requirements for diverse routing to a central host computer? Are there any special port
redundancy requirements?
2. Identify required legacy support.
Are STP bridges used in the network? These bridges do not support rapid transitioning to
forwarding. If these bridges are present can they be re-deployed closer to the network edge?
3. Identify edge ports and ports with half duplex/shared media restrictions.
Ports that connect to host computers, IEDs and controllers may be set to edge ports in order to
guarantee rapid transitioning to forwarding as well as reduce the number of topology change