Appendix F
Flow Control Background
Flow control refers to the techniques used by computer devices and multiplexers to stop and restart the flow of data
from each other. Flow control is necessary so that a channel device does not receive more data than it can handle or
vice versa (the MultiMux receives more data than its buffers can accommodate). Flow control by the mux to control data
flow from a channel device is called Mux Initiated Flow Control. Such flow control might be needed if a mux was
connected to a minicomputer that could output more data than the mux could handle. Flow control by the channel
device to control data flow from the mux is called Channel Device Initiated Pacing. Such pacing might be required by a
printer channel device which could not print data as fast as the mux might send it or might go off-line for some reason
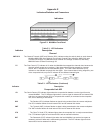
like running out of paper. To state it simply, Flow Control is something the mux does to the channel device, while
pacing is something the channel device does to the mux.
DATA
DATA
CHANNEL DEVICE
INITIATED PACING
Channel
Device
Channel
Device
Mux
Mux
MUX INITIATED
FLOW CONTROL
Flow control stops the
input of data to the mux
Pacing stops the output
of data from the mux
Flow control can be software or hardware based. In software flow control, special characters (Xon and Xoff) are used to
stop and start the flow of data. In hardware flow control the Clear To Send (CTS) signal on the RS232C interface (pin
5) is brought low to stop data and high to restart it. When you select a flow control method with a mux command you
are also selecting the corresponding pacing method.
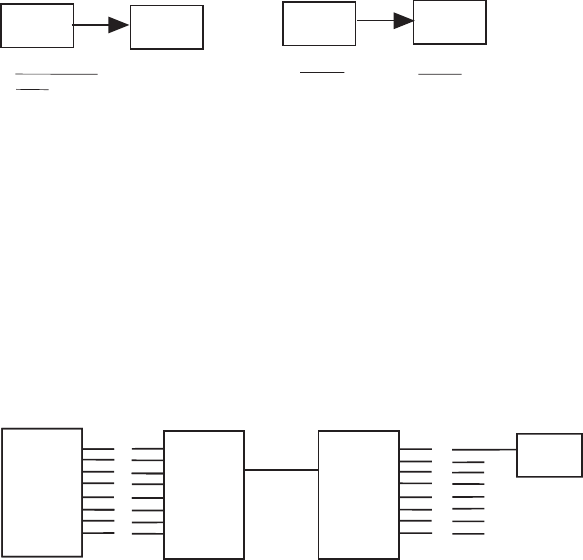
In the example below we have an eight port multi-user minicomputer connected to a MultiMux on one end of a link and
seven terminals plus a printer connected to another MultiMux on the other end of the link. The MultiMux at the printer
end needs Flow Control and Pace on the printer channel to stop and restart data from the minicomputer. The MultiMux
at the minicomputer end needs Flow Control on to all channels to stop and restart data from the minicomputer so that
the muxs buffer capacity is not exceeded. We chose Xon/Xoff flow control for this example and are setting pace ON
for all channel devices.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Mux
Link
Channel
NODE 1
Mini-
Computer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Channel
Mux
Link
Mux
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PC
PC
PC
PC
PC
PC
PC
Printer
Channel
NODE 1 NODE 2
Mini-
Computer
MiniComputer Flow Control