12-8 User’s Reference Guide
Parts of a filter
A filter consists of criteria based on packet attributes. A typical filter can match a packet on any one of the
following attributes:
■ The source IP address (where the packet was sent from)
■ The destination IP address (where the packet is going)
■ The type of higher-layer Internet protocol the packet is carrying, such as TCP or UDP
Port numbers
A filter can also match a packet’s port number attributes, but only if the filter’s protocol type is set to TCP or
UDP, since only those protocols use port numbers. The filter can be configured to match the following:
■ The source port number (the port on the sending host that originated the packet)
■ The destination port number (the port on the receiving host that the packet is destined for)
By matching on a port number, a filter can be applied to selected TCP or UDP services, such as Telnet, FTP, and
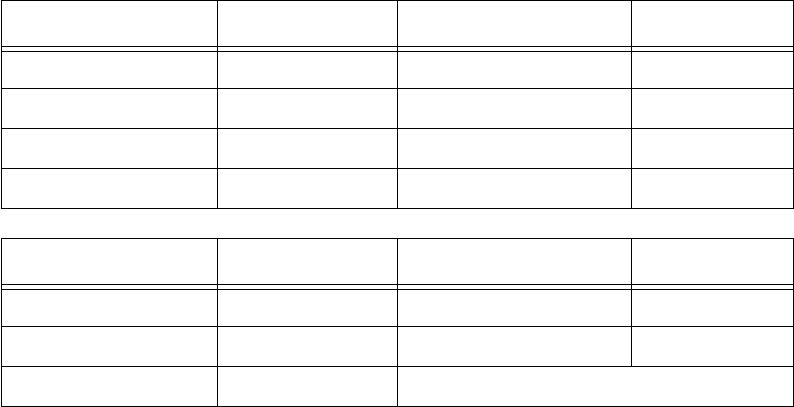
World Wide Web. The tables below show a few common services and their associated port numbers..
Port number comparisons
A filter can also use a comparison option to evaluate a packet’s source or destination port number. The
comparison options are:
No Compare: No comparison of the port number specified in the filter with the packet’s port number.
Not Equal To: For the filter to match, the packet’s port number cannot equal the port number specified in the
filter.
Less Than: For the filter to match, the packet’s port number must be less than the port number specified in the
filter.
Less Than or Equal: For the filter to match, the packet’s port number must be less than or equal to the port
number specified in the filter.
Internet service TCP port Internet service TCP port
FTP 20/21 Finger 79
Telnet 23 World Wide Web 80
SMTP (mail) 25 News 144
Gopher 70 rlogin 513
Internet service UDP port Internet service UDP port
Who Is 43 TFTP 69
World Wide Web 80 who 513
SNMP 161


















