Understanding IP Addressing D-11
Routers B and C (which could also be Netopia R310s) serve the two remote networks that are subnets of
a.b.c.0. The subnetting is accomplished by configuring the Netopia R310 with connection profiles for Routers B
and C (see the following table).
The Netopia R310’s connection profiles for Routers B and C create entries in its IP routing table. One entry
points to the subnet a.b.c.128, while a second entry points to the subnet a.b.c.248. The IP routing table might
look similar to the following:
Let’s see how a packet from the Internet gets routed to the host with IP address a.b.c.249, which is served by
Router C. The packet first arrives at Router A, which delivers it to its local network (a.b.c.0). The packet is then
received by the Netopia R310, which examines its destination IP address.
The Netopia R310 compares the packet’s destination IP address with the routes in its IP routing table. It begins
with the route at the bottom of the list and works up until there’s a match or the route to the default gateway is
reached.
When a.b.c.249 is masked by the first route’s subnet mask, it yields a.b.c.248, which matches the network
address in the route. The Netopia R310 uses the connection profile associated with the route to connect to
Router C, and then forwards the packet. Router C delivers the packet to the host on its local network.
Connection profile Remote IP address Remote IP mask
Bits available for host
address
for Router B a.b.c.128 255.255.255.192 7
for Router C a.b.c.248 255.255.255.248 3
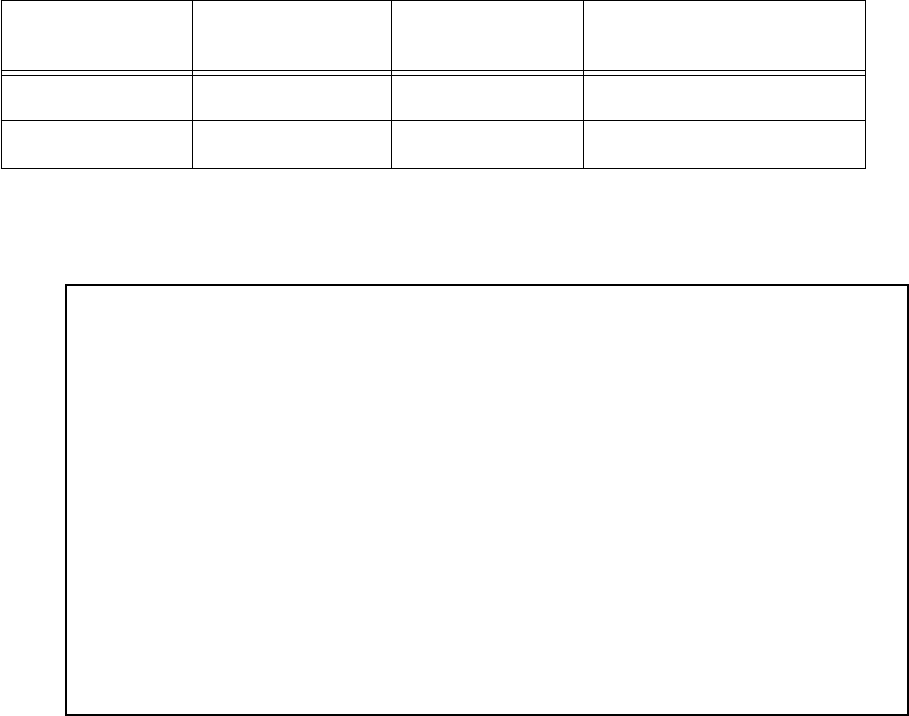
IP Routing Table
Network Address-Subnet Mask-----via Router------Port--Age--------Type------
----------------------------------SCROLL UP--------------------------------
0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 a.b.c.1 WAN 3719 Management
127.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 127.0.0.1 lp1 6423 Local
a.b.c.128 255.255.255.192 a.b.c.128 WAN 5157 Local
a.b.c.248 255.255.255.248 a.b.c.248 WAN 6205 Local
---------------------------------SCROLL DOWN-------------------------------
UPDATE


















