Understanding Netopia NAT Behavior E-3
When the Netopia R310 receives this IP packet, it can not simply forward it to the WAN interface and the
Internet since the IP addresses on the LAN interface are not valid or globally unique for the Internet. Instead the
Netopia R310 has to change the IP packet to reflect the IP address that was acquired on the WAN interface
from the ISP.
The Netopia R310 will first substitute the source IP address with the IP address that was acquired on the WAN
interface which in this case is 200.1.1.40. Next the Netopia R310 will substitute the source TCP or UDP port
with a TCP or UDP port from within a specified range maintained within the Netopia R310. And finally the
modified IP packet's checksum is recalculated (as specified in RFC 1631) and the packet is transmitted across
the WAN interface to its destination, the WWW Server on the Internet.
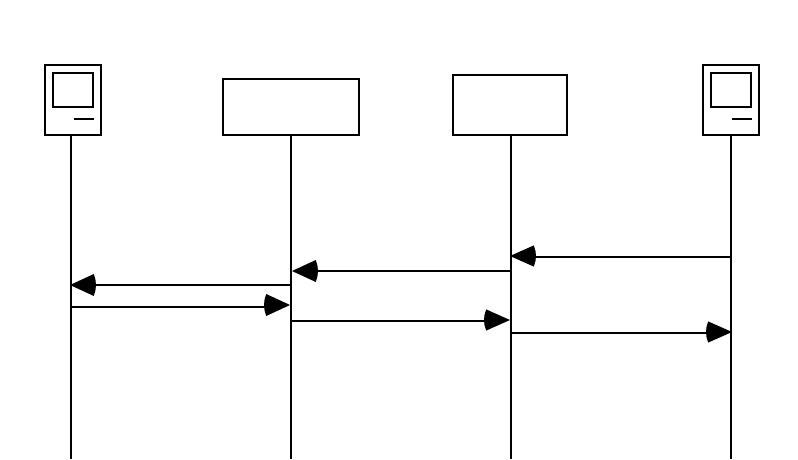
If the send and response IP packets were drawn out, this process would look like the following:
As you can see, the IP packet from Workstation A is sent to the Netopia R310 and the source IP address is
substituted with 200.1.1.40 and the source port is substituted with 5001, then the IP packet checksum is
recalculated. When this modified packet reaches the WWW Server on the Internet, the WWW Server responds
and sends the IP packet back to destination IP address 200.1.1.40 and destination port 5001.
When the Netopia R310 receives this IP packet from the WWW Server, the Netopia R310 replaces the
destination IP address with 192.168.5.2, the address for Workstation A. The port is changed back to 400, the
IP packet checksum is recalculated, and the IP packet is sent to Workstation A on the Netopia R310s LAN
interface.
The reasons for the IP address changes are obvious from the diagram above but what is not so obvious is why
the TCP or UDP source ports need to be changed as well. These are changed and maintained in an internal
table so the Netopia R310 can determine which host on the local LAN interface sent the IP packet and what
host the response from the WAN interface is going to go to on the LAN interface. This becomes especially
important when two or more hosts on the LAN interface are accessing the same type of service on the Internet,
like a WWW Server (Port 80), for example.
Netopia
Router
Wkstn A to Netopia
Src IP: 192.168.5.2
Dst IP: 163.176.4.32
Src Port:: 400
Dst Port:: 80
Workstation A
192.168.5.2
Netopia Router
LAN: 192.168.5.1
WAN: 200.1.1.40
Netopia to ISP Router
Src IP: 200.1.1.40
Dst IP: 163.176.4.32
Src Port:: 5001
Dst Port:: 80
ISP Router to WWW
Src IP: 200.1.1.40
Dst IP: 163.176.4.32
Src Port:: 5001
Dst Port:: 80
WWW to ISP Router
Src IP: 163.176.4.32
Dst IP: 200.1.1.40
Src Port:: 80
Dst Port:: 5001
ISP Router to Netopia
Src IP: 163.176.4.32
Dst IP: 200.1.1.40
Src Port:: 80
Dst Port:: 5001
Netopia to Wkstn A
Src IP: 163.176.4.32
Dst IP: 192.168.5.2
Src Port:: 80
Dst Port:: 400
ISP Router
200.1.1.1
WWW Server
163.176.4.32


















