5–Fibre Channel over IP
Configuring FCIP
5-14 ISR651101-00 G
Data Compression
Data compression is an option that in some configurations can provide a data
throughput rate greater than the capability of the IP link. The iSR6200 is capable
of compressing data at rates up to 190Mbps. The iSR6200 can automatically
enable or disable compression to achieve maximum throughput on a real-time
basis, depending on the compressibility of the data and the configured bandwidth
for the FCIP route. QLogic recommends that you always enable data compression
and monitor the resulting performance to determine improvement. The FCIP route
bandwidth must be correctly configured to realize the affects of automatic
compression.
Bandwidth Limiting
The router provides the ability to set the maximum bandwidth used by an FCIP
route. This setting is very important because most WANs do not support the
1-gigabit data rate of the router’s GE ports. Bandwidth limiting is also needed for
those configurations where the FCIP route is only allocated a portion of the total
bandwidth.
When a configuration requires that the bandwidth available to the FCIP route be a
percentage of the total WAN bandwidth, it is important to correctly calculate the
bandwidth and set it accordingly. For instance if the FCIP route is being allocated
50 percent of an OC-3 link (150Mbps link), the route bandwidth setting should be
as follows:
Bandwidth Allocated = 50% × Link Rate
75Mbps = 0.5 × 150Mbps
For more information, see “Configuring an FCIP Route Using the CLI” on
page 5-3.
TCP Window Settings
The TCP window size defines the amount of data sent before seeing an
acknowledgement. It is used to avoid overwhelming the receiver and still maintain
a constant flow of data. The TCP window size is typically calculated based on the
RTT and WAN speed.
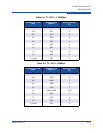
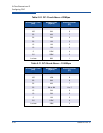
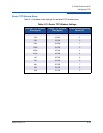
The following tables show the suggested TCP window size settings for IP links
based on link speed and RTT.
NOTE:
The bandwidth parameter should never be set higher than the total WAN
bandwidth; otherwise, performance suffers due to WAN congestion
(dropped packets).