PID Loop Configuration
The inverter’s PID loop algorithm is configurable for various applications.
P
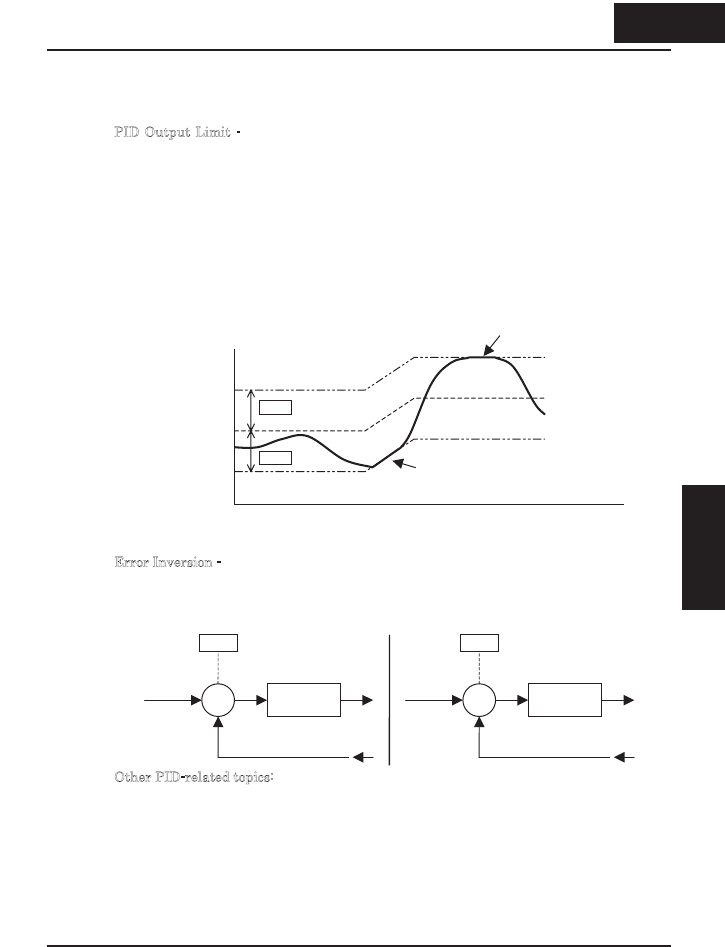
ID Output Limit - The PID loop controller has a built-in output limit function. This
function monitors the difference between the PID setpoint and the loop output (inverter
output frequency), measured as a percentage of the full scale range of each. The limit is
specified by parameter A078.
x When the difference |(Setpoint – loop output)| is smaller than or equal to the A078
limit value, the loop controller operates in its normal linear range.
x When the difference |(Setpoint – loop output)| is larger than the A078 limit value,
the loop controller changes the output frequency as needed so that the difference
does not exceed the limit.
The diagram below shows PID setpoint changes and the related output frequency
behavior when a limit value in A078 exists.
E
rror Inversion - In typical heating loops or ventilation loops, an increase in energy into
the process results in an
increasing
PV. In this case, the Loop Error = (SP – PV). For
cooling loops, an increase in energy into the process results in a
decreasing
PV. In this
case, the Loop Error = –(SP – PV). Use A077 to configure the error term.
O
ther PID-related topics:
x “PID Control” on page 3–22
x “PID ON/OFF and PID Clear” on page 4–26
x “Output Deviation for PID Control” on page 4–4
3
x “PID Second Stage Output” on page 4–4
7
t
Output limit
PID Setpoint
Output limit
Limit imposed
on output
Limit imposed
on output
A078
A078
%
Output freq.
6
PID
calculation
SP
+
Error Freq.
PV
-
PV from process with
positive correlation
A077
=00
6
PID
calculation
SP
-
Error Freq.
PV
+
PV from process with
negative correlation
A077
=01
459
Inverter Mounting
and installation
4 59
Operations and
Monitoring


















