6 P—P28 and P128 Series Lube Oil Controls with Built-in Time Delay Relay Product/Technical Bulletin
*When crankcase heater is used, disconnect
j
umper from 2 to M
and reconnect 2 to L.
*
240V
3-phase
Crankcase
Heater
When Used*
Runli
g
ht
if Used
Alarm
if Used
Additional controls
in this line onl
y
.
Start
Stop
Motor
P28 or P128
240
120
3
1
2
L
M
A
C
2
C
3
L
1
L
2
L
3
T
1
T
2
T
3
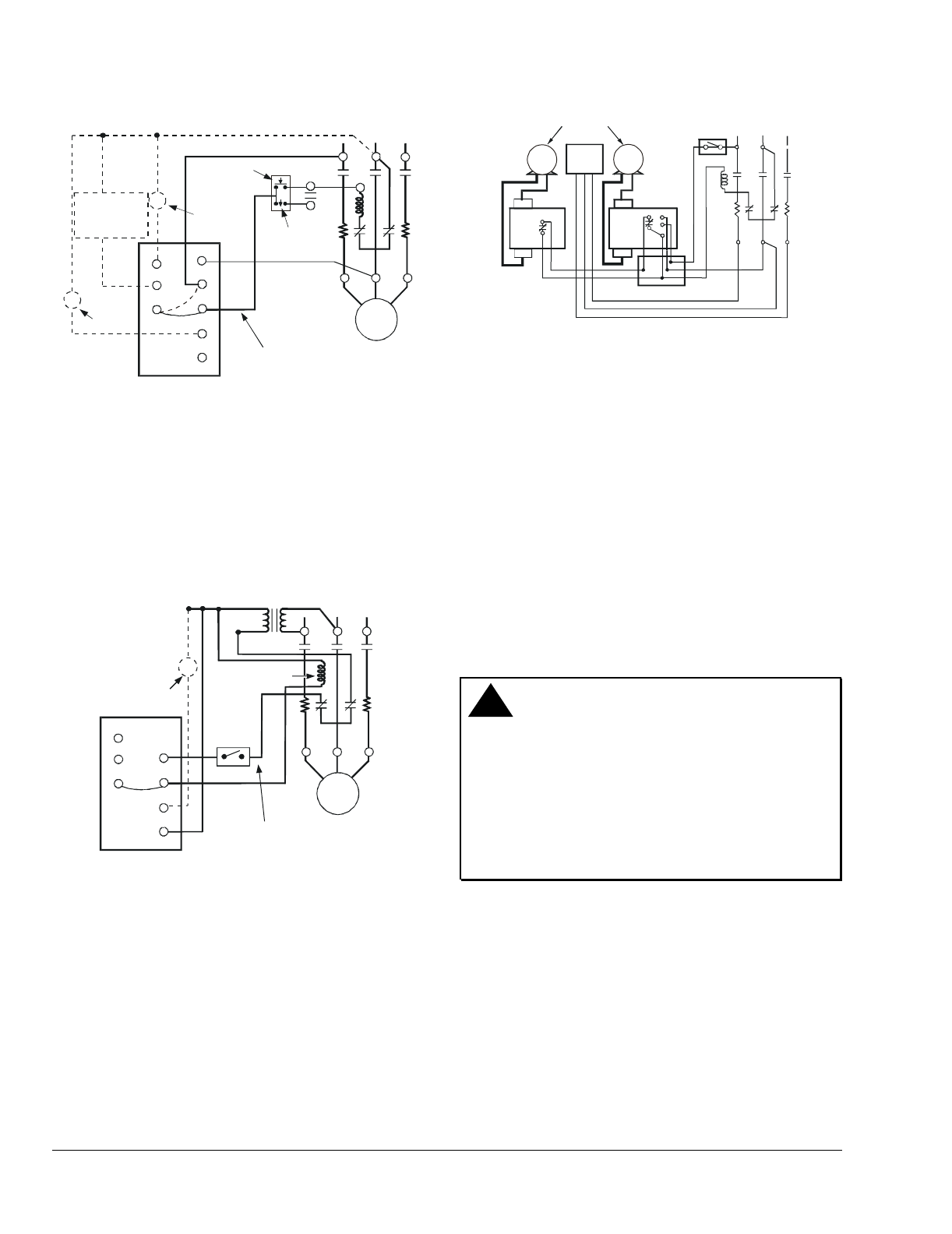
Figure 8: P28 or P128 Where Manual “Start-Stop”
Pushbutton Station is Used (Jumper between
2 and M [or L] must be field installed.)
*12 volt also available.
Transformer
240V
3-phase
Starter Coil
Operatin
g
Control
Motor
Additional controls
in this line onl
y
.
P28 or P128
Alarm
if Used
3
1
2
L
M
A
24*
L
1
L
2
L
3
T
1
T
2
T
3
Figure 9: P28 or P128 Where 24V Control Circuit
Power is from a Step-down Transformer (Jumper
between 2 and M must be field installed.)
Note:This s
y
stem would provide shutdown on low
lube oil pressure in either of two compressors
operated b
y
the common motor.
Oil
Low
Oil
Low
P74AA
P28/P128
Compressor
Motor
Junction Box
1
2
240
M
L
T
1
T
2
T
3
Operatin
g
Control
240 V
L
1
L
2
L
3
Figure 10: P28 or P128 and P74AA Wired for an
Oil Pressure Control System Where One Motor
Operates Two Compressors
Adjustments
The P28 and P128 controls are shipped with a cut-out
pressure differential of 9 psi (62 kPa). However, the
controls can be adjusted according to the compressor
manufacturer’s specifications.
Note: When the controls are shipped as an
accessory to the compressor unit, time delay
and cut-out pressure are set to manufacturer’s
specifications. Replacement controls should
duplicate the manufacturer’s specifications.
!
CAUTION: Equipment damage hazard.
To avoid damage to the
compressor, obtain the
compressor manufacturer’s net
oil bearing pressure
specifications as soon as
possible. If necessary, reset the
cut-out pressure difference to the
manufacturer’s specifications.
When the manufacturer’s specifications are not known,
proceed as follows to set the cut-out pressure
differential:
1. With the compressor running, read the oil pressure
and the crankcase pressure.
2. Subtract the crankcase pressure reading from the
oil pressure pump discharge reading. This is the
net oil pressure to the bearings.