Router Node 7
packet size. This would only enable a wide node to handle approximately 7.5
MB/s of IP traffic.
Since Ascend’s business depends on keeping pace with networking
technology, they already support the major interfaces today. The 9077 will be
able to take advantage of any new interfaces that are developed in the future
as well, with no further development time or money expended.
With some interfaces requiring up to 5 slots, even a wide node can run out of
available slots. This forces additional nodes to be added even if there are no
performance limitations in the current configuration.
Since there are no hot plug capabilities with an SP node, any failure means
downtime on all interfaces configured in that node, and at times a lengthy
maintenance procedure. Redundancy is not built into the SP node’s
architecture.
These facts are illustrated in Figure 2:
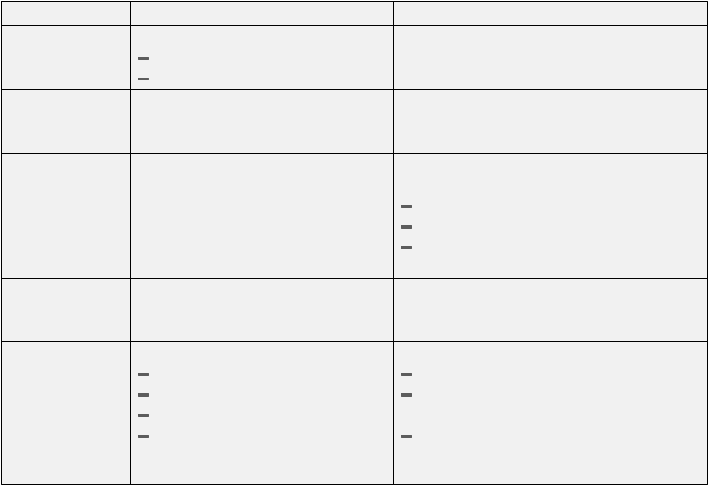
Figure 2. Functional Comparison
SP Node 9077
Bus
Shared
1 MCA per thin node
2 MCA per wide node
Non-blocking Crosspoint Switch
250 ns path setup
Route Table
Centralized
Cache,Software Based
Cache hits <50% typical
Independent lookups per card
Hardware based, <2.5 µs
150,000 route capacity per card
Scalability
Single port per card
Single CPU
Limited by shared bus
High per card port density
Per card
Processors
Route Tables
Lookup engines
Each card has dedicated bandwidth
Throughput
5000 pps
30 MB/s per thin node
65 MB/s per wide node
Up to 130,000 pps
100 MB/s per card slot, full duplex
Support
No support for:
HSSI
ATM OC12
Sonet
Multiple SP Switch Adapters
Support for:
multiple SP Switch interfaces
High-speed networks such as
HIPPI
Protocols


















