E6581301
A-19
1
In circuit configuration 1, the brake is turned on and off through MC2 and MC3. If the circuit is configured in some
other way, the overcurrent trip may be activated because of the locked rotor current when the brake goes into
operation.
Circuit configuration 2 uses low-speed signal OUT1 to turn on and off the brake. Turning the brake on and off with a
low-speed detection (OUT1 function) may be better in such applications as elevators. Please confer with your
Toshiba distributor before designing the system.
Measures to protect motors against surge voltages
In a system in which a 400V-class inverter is used to control the operation of a motor, very high surge voltages may
be produced. When applied to the motor coils repeatedly for a long time this can cause deterioration of their
insulation, depending on the wire length, wire routing and types of wires used. Here are some examples of
measures against surge voltages.
(1) Lower the inverter’s carrier frequency.
(2) Set the parameter
H
(Carrier frequency control mode selection) to
or
.
(3) Use motors with a high dielectric strength.
(4) Insert an reactor or a surge voltage suppression filter between the inverter and the motor.
1.4.2 Inverters
Protecting inverters from overcurrent
The inverter has an overcurrent protection function. The programmed current level is set to the inverter's maximum
applicable motor. If the motor used has a small capacity, the stall prevention level, overcurrent level and the motor
electronic thermal protection must be readjusted. If adjustment is necessary, refer to Section 5.14, and make
adjustments as directed.
Inverter capacity
Do not operate a large capacity motor with a small capacity (kVA) inverter even with light loads. Current ripple will
raise the output peak current making it easier to set off the overcurrent trip.
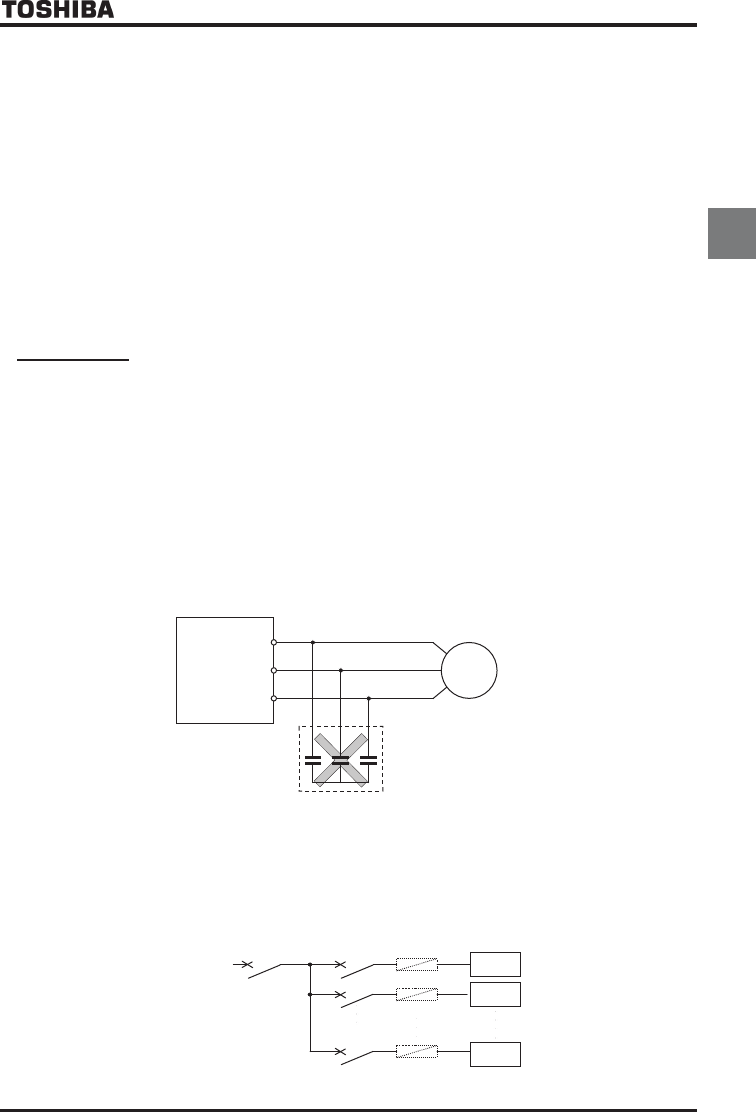
Power factor correction capacitor
Power factor correction capacitors cannot be installed on the output side of the inverter. When a motor is run that
has a power factor correction capacitor attached to it, remove the capacitors. This can cause inverter malfunction
trips and capacitor destruction.
Remove the power factor
correction capacitor and surge
absorber
Power factor correction
capacitor
U
V
W
Inverter
IM
Operating at other than rated voltage
Connections to voltages other than the rated voltage described in the rating label cannot be made. If a connection
must be made to a power supply other than one with rated voltage, use a transformer to raise or lower the voltage
to the rated voltage.
Circuit interrupting when two or more inverters are used on the same power line.
MCCB1
MCCBn
MCCB3
MCCB2
INV1
INV2
INVn
(Circuit interrupting fuse)
Breaking of selected inverter