P-202H Plus v2 Support Notes
12. Using SNMP
1. SNMP Overview
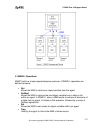
The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an applications-layer
protocol used to exchange the management information between network
devices (e.g., routers). By using SNMP, network administrators can more easily
manage network performance, find and solve network problems. The SNMP is a
member of the TCP/IP protocol suite, it uses the UDP to exchange messages
between a management Client and an Agent, residing in a network node.
There are two versions of SNMP: Version 1 and Version 2. ZyXEL supports
SNMPv1. Most of the changes introduced in Version 2 increase SNMP's security
capabilities. SNMP encompasses three main areas:
1. A small set of management operations.
2. Definitions of management variables.
3. Data representation.
The operations allowed are: Get, GetNext, Set, and Trap. These functions
operates on variables that exist in network nodes. Examples of variables include
statistic counters, node port status, and so on. All of the SNMP management
functions are carried out through these simple operations. No action operations
are available, but these can be simulated by the setting of flag variables. For
example, to reset a node, a counter variable named 'time to reset' could be set to
a value, causing the node to reset after the time had elapsed.
SNMP variables are defined using the OSI Abstract Syntax Notation One
(ASN.1). ASN.1 specifies how a variable is encoded in a transmitted data frame;
it is very powerful because the encoded data is self-defining. For example, the
encoding of a text string includes an indication that the data unit is a string, along
with its length and value. ASN.1 is a flexible way of defining protocols, especially
for network management protocols where nodes may support different sets of
manageable variables.
The net of variables that each node supports is called the Management
Information Base (MIB). The MIB is made up of several parts, including the
Standard MIB, specified as part of SNMP, and Enterprise Specific MIB, which are
defined by different manufacturer for hardware specific management.
The current Internet-standard MIB, MIB-II, is defined in RFC 1213 and contains
171 objects. These objects are grouped by protocol (including TCP, IP, UDP,
SNMP, and other categories, including 'system' and 'interface.'
All contents copyright © 2006 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
110