“A” Group: Standard Functions
Configuring Drive
Parameters
3–22
PID Control When enabled, the built-in PID loop calculates an ideal inverter output value to cause a loop
feedback process variable (PV) to move closer in value to the setpoint (SP). The current
frequency command serves as the SP. The PID loop algorithm will read the analog input for the
process variable (you specify either current or voltage input) and calculate the output.
• A scale factor in A075 lets you multiply the PV by a factor, converting it into engineering
units for the process.
• Proportional, integral, and derivative gains are all adjustable.
• Optional – You can assign an intelligent input terminal the option code 23, PID Disable.
When active, this input disables PID operation. See “
Intelligent Input Terminal Overview”
on page 3–49.
•See “
PID Loop Operation” on page 4–71 for more information.
NOTE: The setting A073 for the integrator is the integrator’s time constant Ti, not the gain.
The integrator gain Ki = 1/Ti. When you set A073 = 0, the integrator is disabled.
“A” Function
Run
Mode
Edit
Lo Hi
Defaults
Units
SRW Display
Func.
Code
Name Description
–FE
(CE)
–FU
(UL)
–FR
(Jpn)
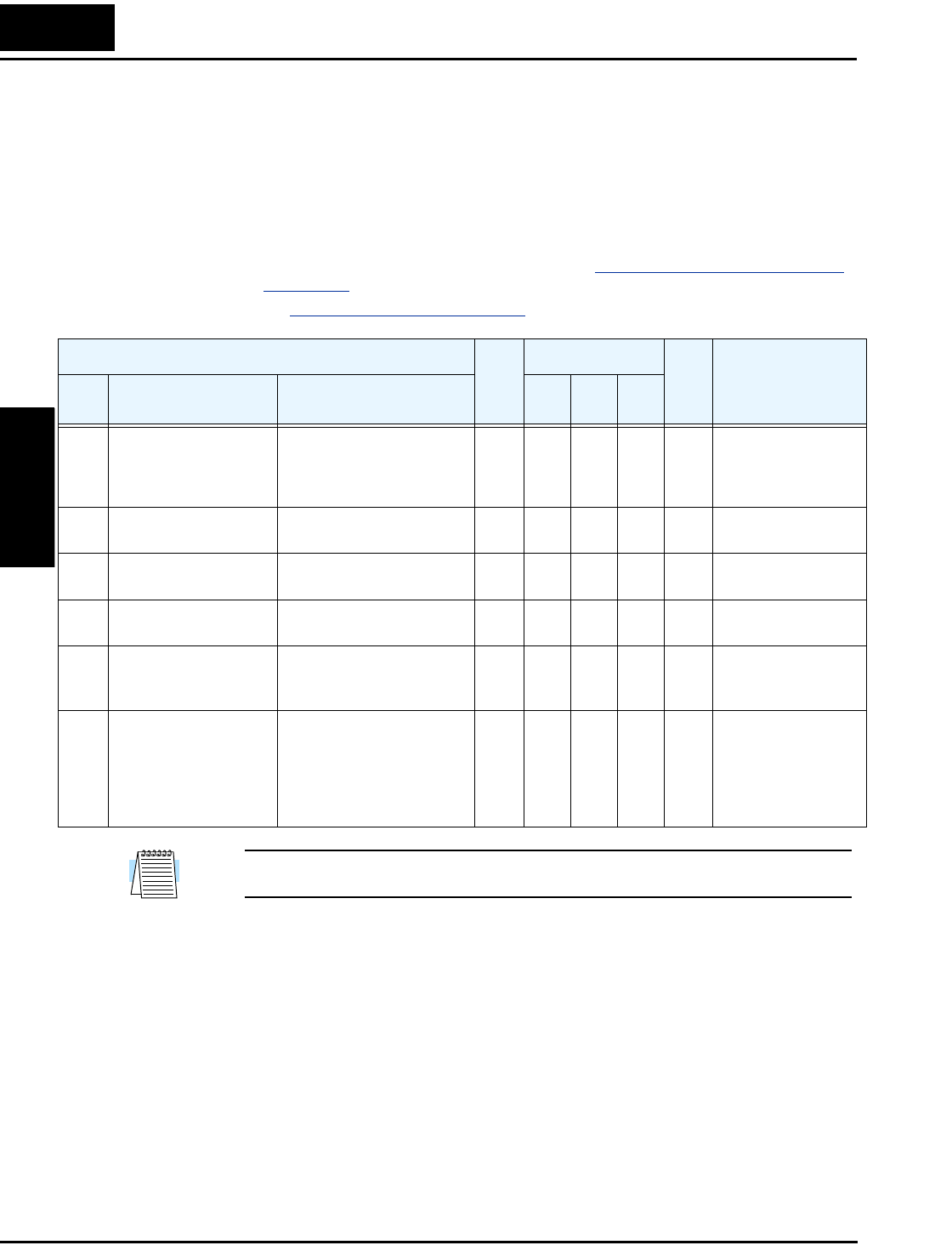
A071 PID Enable Enables PID function,
two option codes:
00 PID operation OFF
01 PID operation ON
✘ ✔ 00 00 00 —
>A071 PID
SW OFF
A072 PID proportional gain Proportional gain has a
range of 0.2 to 5.0
✔ ✔ 1.0 1.0 1.0 —
>A072 PID
P 1.0
A073 PID integral time
constant
Integral time constant has a
range of 0.0 to 3600 seconds
✔ ✔ 1.0 1.0 1.0 sec.
>A073 PID
I 0001.0s
A074 PID derivative time
constant
Derivative time constant has
a range of 0.0 to 100 seconds
✔ ✔ 0.0 0.0 0.0 sec.
>A074 PID
D 000.00
A075 PV scale conversion Process Variable (PV) scale
factor (multiplier), range of
0.01 to 99.99
✘ ✔ 1.00 1.00 1.00 —
>A075 PID
CONV 001.00
A076 PV source setting Selects source of Process
Variable (PV), option codes:
00 [OI] terminal (current
input)
01 [O] terminal (voltage
input)
✘ ✔ 00 00 00 —
>A076 PID
INPUT OI


















