Chapter 5 Device Network Settings
Vantage CNM User’s Guide
61
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
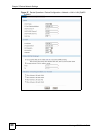
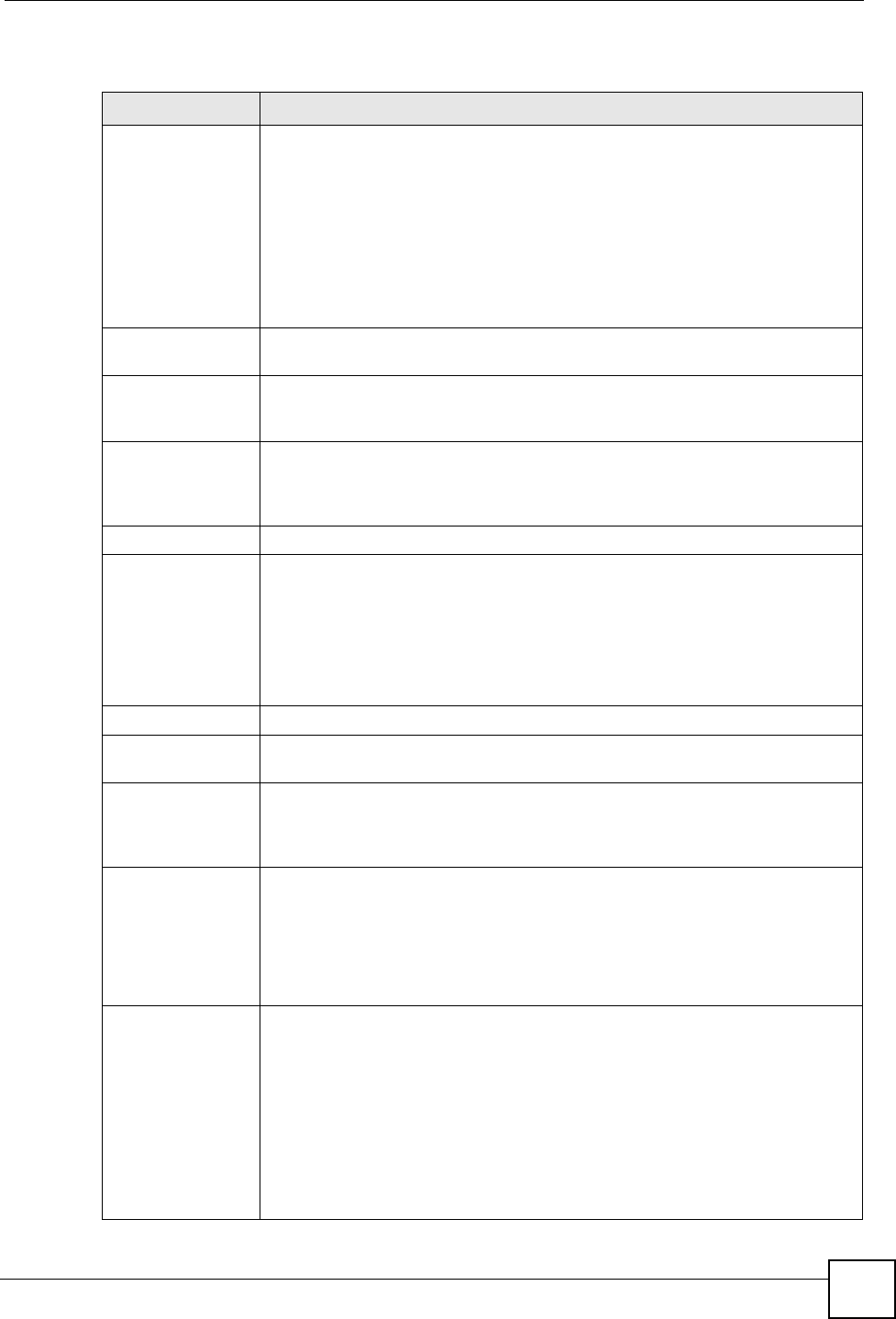
Table 13 Device Operation > Device Configuration > LAN > LAN (ZyNOS ZyWALL)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DHCP Mode DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows
individual clients (workstations) to obtain TCP/IP configuration at startup from a
server. Unless you are instructed by your ISP, leave this field set to Server. When
configured as a server, the device provides TCP/IP configuration for the clients.
When set as a server, fill in the IP Pool Starting Address and Pool Size fields.
Select Relay to have the device forward DHCP requests to another DHCP
server. When set to Relay, fill in the DHCP Server IP field.
Select None to stop the device from acting as a DHCP server. When you select
None, you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computers
must be manually configured.
IP Pool Starting
Address
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool.
DHCP Server IP Type the IP address of the DHCP server to which you want the device to relay
DHCP requests. Use dotted decimal notation. Alternatively, click the right mouse
button to copy and/or paste the IP address.
DHCP WINS
Server 1, 2
Type the IP address of the WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) server that
you want to send to the DHCP clients. The WINS server keeps a mapping table
of the computer names on your network and the IP addresses that they are
currently using.
Pool Size This field specifies the size, or count of the IP address pool.
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Third DNS Server
These fields are enabled if the DHCP Mode is Server. Specify the DNS servers
that are provided to DHCP clients.
Select From ISP if you want the device to use corresponding DNS server
provided by the ISP.
Select User-Defined and specify the IP address if you want the device to use the
specific DNS server.
Select DNS Relay if you want the device to
TCP/IP
IP Address Type the IP address of the device in dotted decimal notation. 192.168.1.1 is the
factory default.
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. The
device automatically calculates the subnet mask based on the IP address that
you assign. Unless you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask
computed by the device, which is 255.255.255.0.
RIP Direction RIP (Routing Information Protocol, RFC1058 and RFC 1389) allows a router to
exchange routing information with other routers. The RIP Direction field controls
the sending and receiving of RIP packets. Select the RIP direction from Both/In
Only/Out Only/None. When set to Both or Out Only, the device broadcasts its
routing table periodically. When set to Both or In Only, it incorporates the RIP
information that it receives; when set to None, it does not send any RIP packets
and ignores any RIP packets received. Both is the default.
RIP Version The RIP Version field controls the format and the broadcasting method of the
RIP packets that the device sends (it recognizes both formats when receiving).
RIP-1 is universally supported but RIP-2 carries more information. RIP-1 is
probably adequate for most networks, unless you have an unusual network
topology. Both RIP-2B and RIP-2M sends the routing data in RIP-2 format; the
difference being that RIP-2B uses subnet broadcasting while RIP-2M uses
multicasting. Multicasting can reduce the load on non-router machines since they
generally do not listen to the RIP multicast address and so will not receive the
RIP packets. However, if one router uses multicasting, then all routers on your
network must use multicasting, also. By default, RIP direction is set to Both and
the Version set to RIP-1.