Appendix 2. Selection
A2 - 11
(5) Selecting the appropriate motor from the short time characteristics (acceleration/
deceleration time constant)
The acceleration/deceleration time constant is calculated using expression (a), and is judged
whether it satisfies the target acceleration/deceleration time constant of 100ms.
(JL+JM)N (32.2+14.0)3000
HF103B: ta=
95.5
0.8TMAX
TU
TF
=
95.5
0.8
21.6
5.3
0.27
= 123.9 (ms)
(J
L+JM)N (32.2+20.0)3000
HF153B: ta=
95.5
0.8TMAX
TU
TF
=
95.5
0.8
35.3
5.3
0.27
= 72.3 (ms)
(J
L+JM)N (32.2+47.9)3000
HF203B: ta=
95.5
0.8TMAX
TU
TF
=
95.5
0.8
41.7
5.3
0.27
= 90.5 (ms)
(J
L+JM)N (32.2+84.7)3000
HF353B: ta=
95.5
0.8TMAX
TU
TF
=
95.5
0.8
59.8
5.3
0.27
= 86.9 (ms)
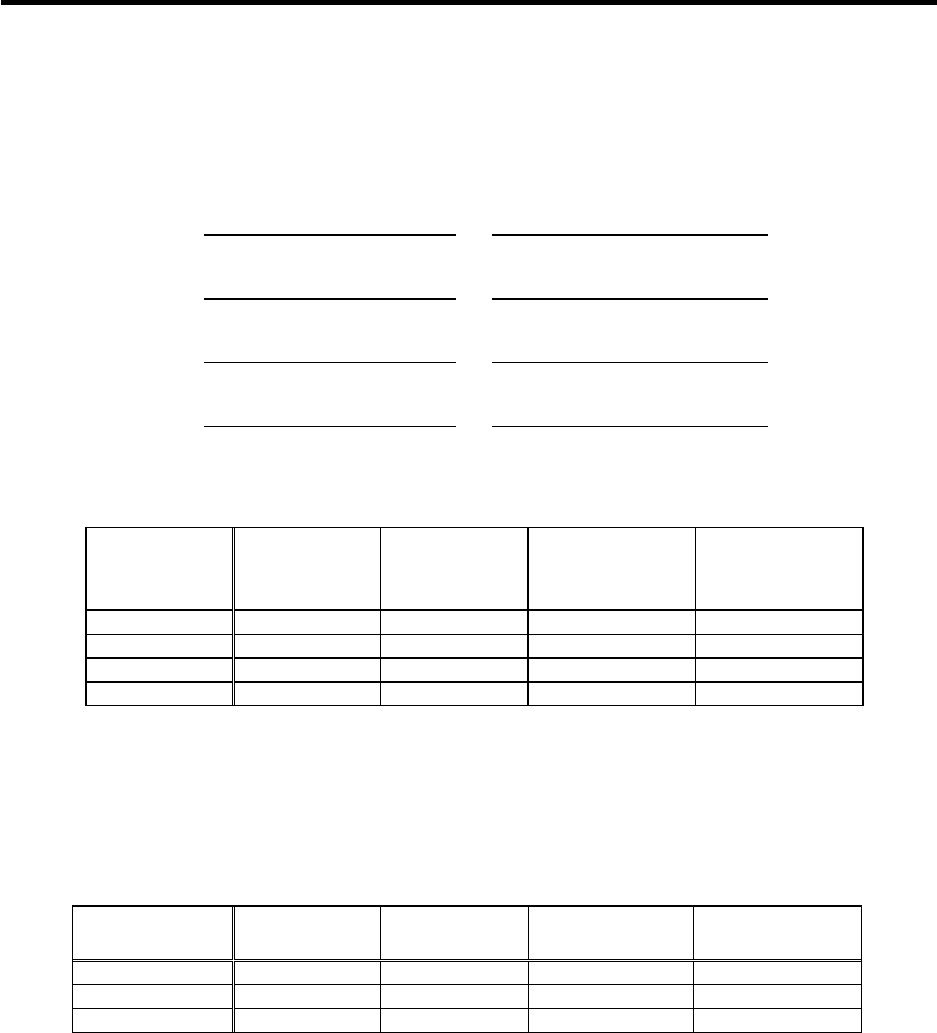
The motor which satisfies the conditions based on the above calculation results is HF153B or more
as shown below.
Motor type
Maximum
torque (N
.
m)
Total inertia
(kg
.
cm
2
)
Acceleration/
deceleration time
constant
[ms]
Judgment
HF103B 21.6 46.2 123.9
HF153B 35.3 52.2 72.3
HF203B 41.7 80.1 90.5
HF353B 59.8 116.9 86.9
(6) Selecting the appropriate motor from the continuous characteristics
Generally, the motor is judged following the typical operation pattern. Because the Z axis is the
vertical axis here, the motor will be judged by the torque during an upward stop.
The unbalance axis torque during a stop should be 60% or less of the stall torque. This is one of the
criteria for motor selection. As shown in the following table, only the HC203B or larger motor satisfies
this criterion. Based on the judgment in steps (4) to (6), the "HF203B" motor is appropriate for the Z
axis.
Motor type Stall torque (N
.
m)
Torque during
stop T
U
+T
F
(kg
.
cm
2
)
Load rate (%) Judgment
HF153B
8.82 5.57 63.2
HF203B
13.7 5.57 40.7
HF353B
22.5 5.57 24.8
