Appendix 8 Old motor specifications
A8 - 20
Appendix 8-7 Dynamic brake characteristics
If a servo alarm that cannot control the motor occurs, the dynamic brakes will function to stop the
servomotor regardless of the parameter settings.
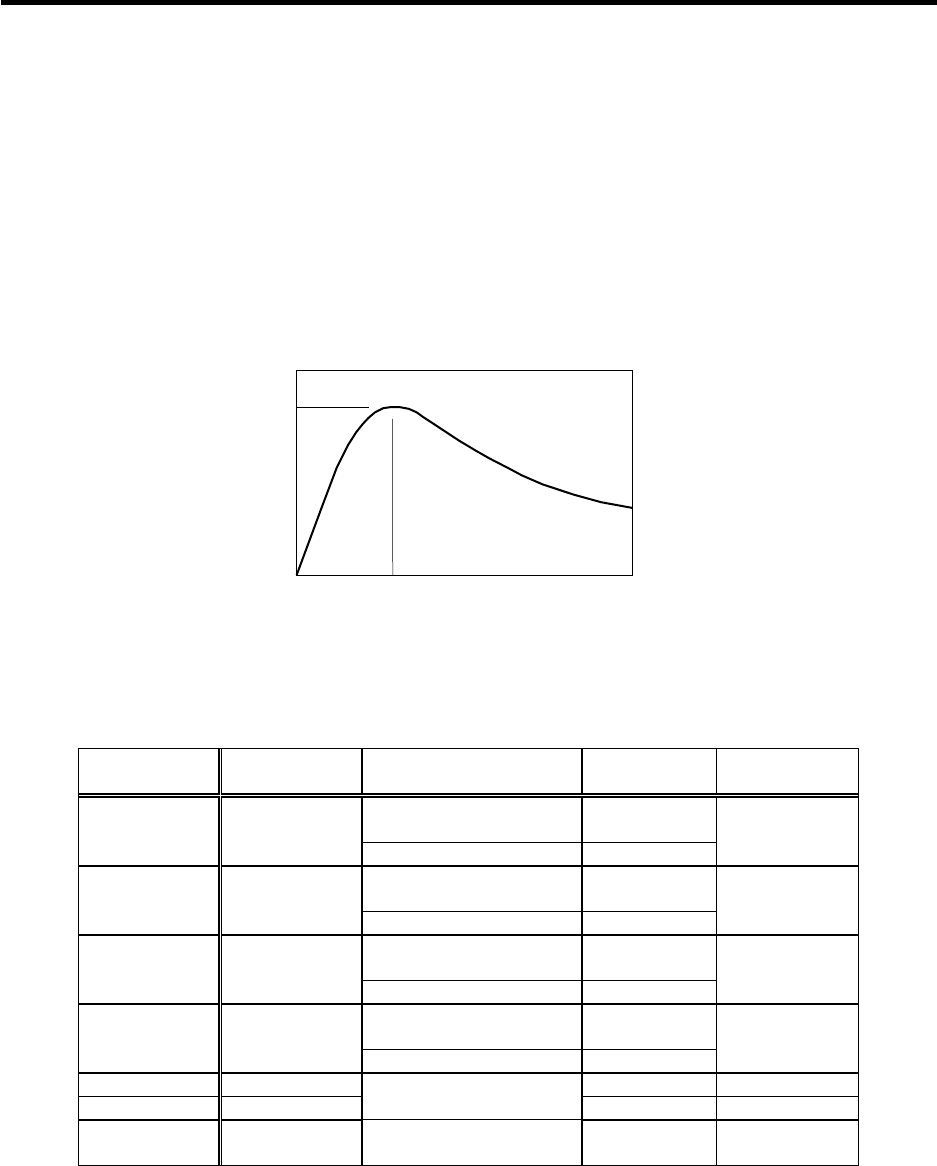
(1) Deceleration torque
The dynamic brake uses the motor as a generator, and obtains the deceleration torque by consuming
that energy with the dynamic brake resistance. The characteristics of this deceleration torque have a
maximum deceleration torque (Tdp) regarding the motor speed as shown in the following drawing. The
torque for each motor is shown in the following table.
Deceleration torque characteristics of a dynamic brake
Max. deceleration torque of a dynamic brake
Motor type
Stall torque
(N
.
m)
Combination
drive unit type
Ndp (r/min) Tdp (N
.
m)
MDS-R-V1-20 to 40
MDS-R-V2-2020 to 4040
1254
HF44 2.00
MDS-R-V2-6040 to 8040 1282
5.43
MDS-R-V1-20 to 40
MDS-R-V2-2020 to 4040
1254
HF74 3.00
MDS-R-V2-6040 to 8040 1369
5.43
MDS-R-V1-20 to 40
MDS-R-V2-2020 to 4040
478
HF53 2.94
MDS-R-V2-6040 to 8040 534
3.96
MDS-R-V1-20 to 40
MDS-R-V2-2020 to 4040
409
HF103 5.88
MDS-R-V2-6040 to 8040 539
10.04
HF153 8.82 541 15.62
HF203 13.7
MDS-R-V1-60 to 80
MDS-R-V2-6040 to 8080
367 15.94
HF353 22.5
MDS-R-V1-60 to 80
MDS-R-V2-6060 to 8080
464 35.24
Tdp
Ndp
Deceleration
torque
Motor speed
0