Chapter 31 ADP
ZyWALL USG 50 User’s Guide
527
Flood Detection
Flood attacks saturate a network with useless data, use up all available
bandwidth, and therefore make communications in the network impossible.
ICMP Flood Attack
An ICMP flood is broadcasting many pings or UDP packets so that so much data is
sent to the system, that it slows it down or locks it up.
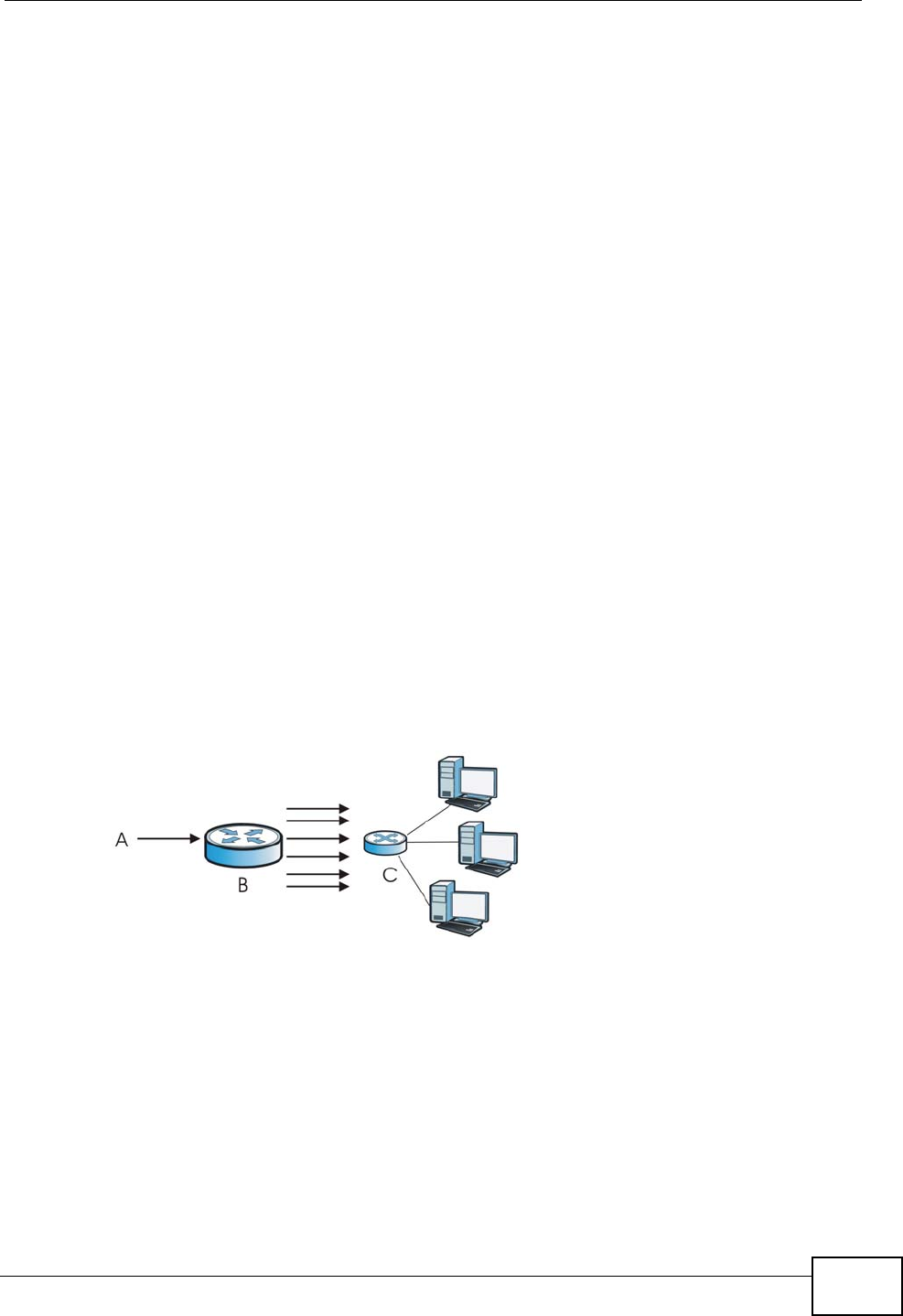
Smurf
A smurf attacker (A) floods a router (B) with Internet Control Message Protocol
(ICMP) echo request packets (pings) with the destination IP address of each
packet as the broadcast address of the network. The router will broadcast the
ICMP echo request packet to all hosts on the network. If there are numerous
hosts, this will create a large amount of ICMP echo request and response traffic.
If an attacker (A) spoofs the source IP address of the ICMP echo request packet,
the resulting ICMP traffic will not only saturate the receiving network (B), but the
network of the spoofed source IP address (C).
Figure 308 Smurf Attack
TCP SYN Flood Attack
Usually a client starts a session by sending a SYN (synchronize) packet to a server.
The receiver returns an ACK (acknowledgment) packet and its own SYN, and then
•ICMP Filtered
Portsweep
• TCP Filtered Distributed
Portscan
• UDP Filtered
Distributed Portscan
• IP Filtered
Distributed Portscan