6-154
ROTC
6.8.5 Rotary table shortest direction control (ROTC)
ROTC
Function
(1) This control functions to enable shortest direction control of the rotary table to the position of
the station number designated by +1 in order to remove or deposit an item whose number
has been designated by +2 on a rotary table with equal divisions of the value designated
by n1.
(2) The item number and station number are controlled as items allocated by counterclockwise
rotation.
(3) The system uses +0 as a counter to instruct it as to what item is at which number counting
from station number 0. Do not rewrite the sequence program data.
Accurate controls will not be possible in cases where users have rewritten the data.
(4) The value of n2 should be less than the number of table divisions specified by n1.
(5) +0 and +1 are A and B phase input signals that are used to detect whether the direction
of the rotary table rotation is forward or reverse.
The direction of rotation is judged by whether the B phase pulse is at its leading or trailing
edge when the A phase pulse is ON:
• When the B phase is at the leading edge: Forward rotation (clockwise rotation)
• When the B phase is at the trailing edge: Reverse rotation (counterclockwise rotation)
: + 0 : Measures the number of table rotations (for system use) (BIN 16 bits)
+ 1 : Call station number (BIN 16 bits)
+ 2 : Call item number (BIN 16 bits)
n1 : Number of divisions of table (2 to 32767) (BIN 16 bits)
n2 : Number of low-speed sections (value from 0 to less than n1) (BIN 16 bits)
: + 0 : A phase input signal (bits)
+ 1 : B phase input signal (bits)
+ 2 : 0 point detection input signal (bits)
+ 3 : High speed forward rotation output signal (for system use) (bits)
+ 4 : Low speed forward rotation output signal (for system use) (bits)
+ 5 : Stop output signal (for system use) (bits)
+ 6 : Low speed reverse rotation output signal (for system use) (bits)
+ 7 : High speed reverse rotation output signal (for system use) (bits)
Setting
Data
Internal Devices
R, ZR
J\
U\G
Zn
Constants
K, H
Other
Bit Word Bit Word
–– –– ––
n1 ––
n2 ––
–– –– ––
Process
High
performance
Universal
Basic
Redundant
Command
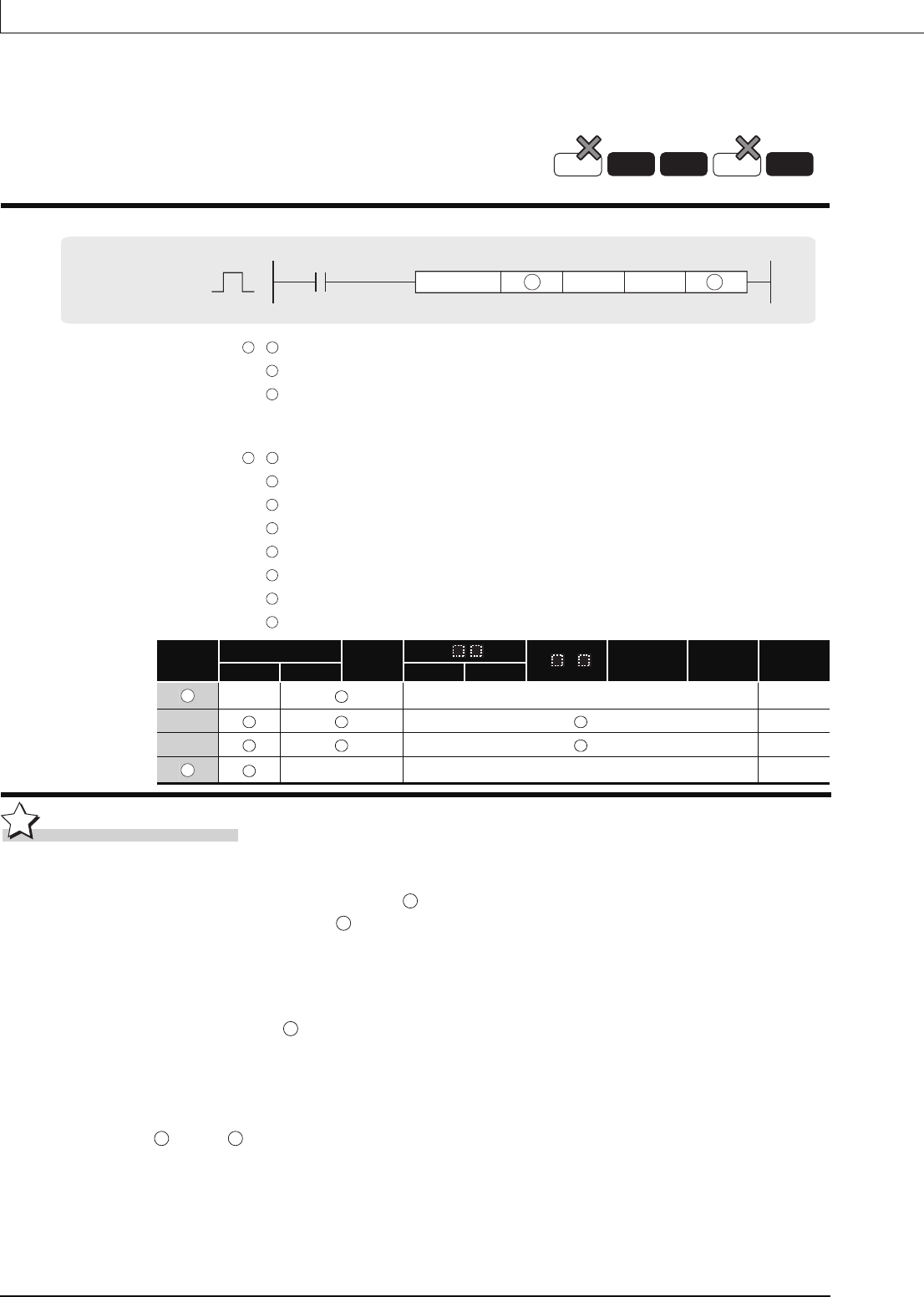
ROTC
n2
n1
S DROTC
S S
S
S
D D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
S
D
S
S
S
D D