3-3
3
4
4
6
7
8
3.2 Designating Data
3.2.1 Using bit data
3.2 Designating Data
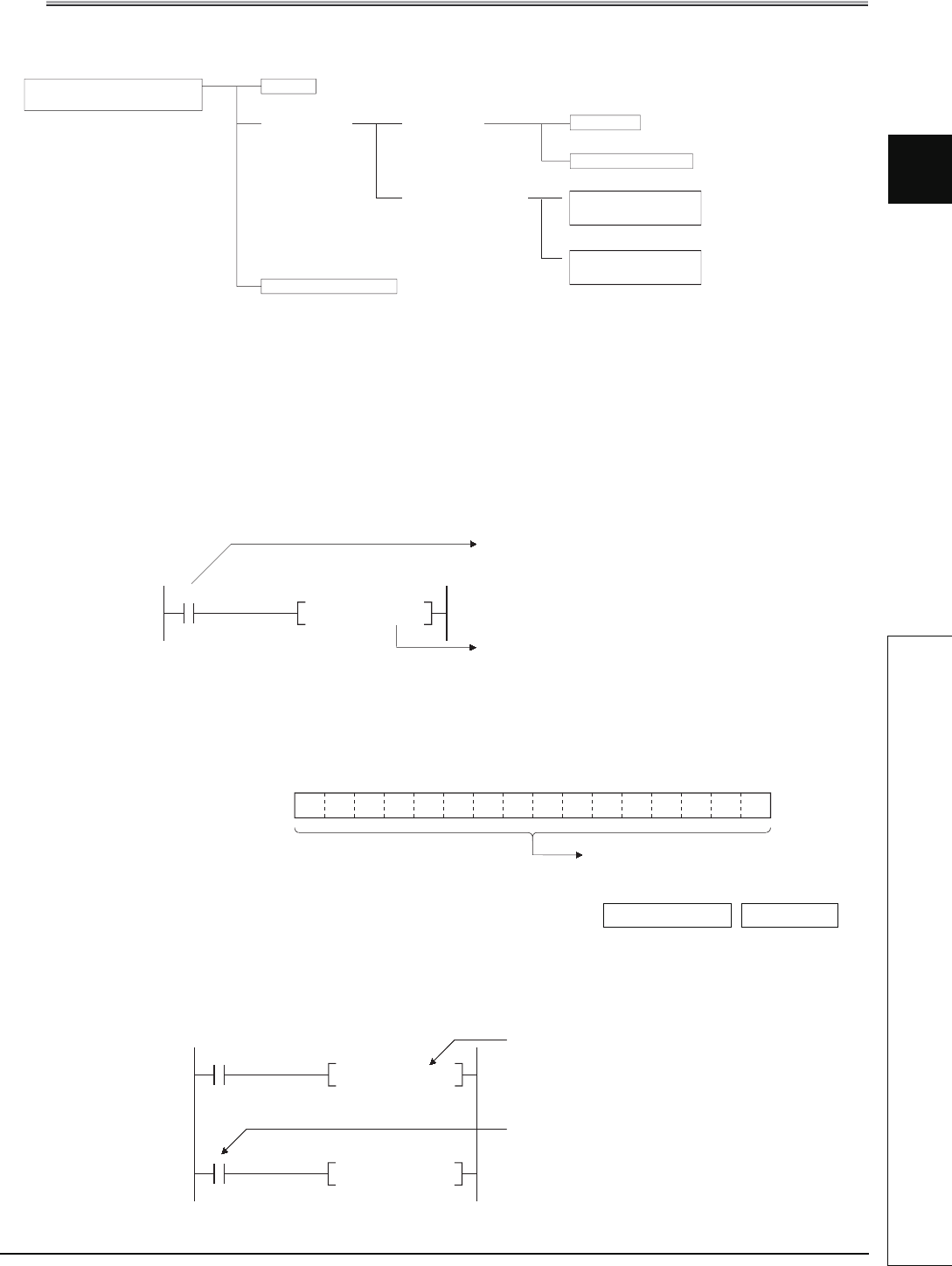
The following six types of data can be used with CPU module instructions.
3.2.1 Using bit data
Bit data is data used in one-bit units, such as for contacts or coils.
"Bit devices" and "Bit designated word devices" can be used as bit data.
(1) When using bit devices
Bit devices are designated in one-point units.
(2) Using word devices
(a) Word devices enable the use of a designated bit number 1/0 as bit data by the
designation of that bit number.
(b) Word device bit designation is done by designating " . ".
(Designation of bit numbers is done in hexadecimal.)
For example, bit 5 (b5) of D0 is designated as D0.5, and bit 10 (b10) of D0 is designated
as D0.A. However, there can be no bit designation for timers (T), retentive timers (ST),
counters (C) or index register (Z). (Example Z0.0 is not available).
Word data
Data that can be handled by
CPU module
Bit data
Numeric data
Character string data
Integer data
Real number
(floating point) data
Single-precision
floating point data
Double-precision
floating point data
Double-word data
.......................Section 3.2.2
...................... Section 3.2.1
.... Section 3.2.4 (1)
.... Section 3.2.4 (2)
...........Section 3.2.3
.... Section 3.2.5
M0
SET Y10
Designation of 1 point
of bit device Y10
Designation of 1 point
of bit device M0
b15b0
1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0 1/0
to
Word device
Each bit of a word device can be
used (1=ON, 0=OFF)
Word device Bit No.
D0.5
SET Y10
Bit designated for word device
(Turns ON Y10 if bit 5 (b5) of D0 is ON (1).)
X0
SET D0.5
Bit designated for word device
(Bit 5 (b5) of D0 is turned ON if X0 is ON.)