3-7
3
4
4
6
7
8
3.2 Designating Data
3.2.3 Using double word data (32 bits)
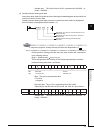
(c) When destination (D) data is a word device
The word device for the destination becomes 0 following the bit designated by digit
designation at the source.
Fig 3.5 Ladder Example and Processing Conducted
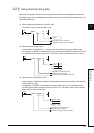
(d) In cases where digit designation is made at the destination (D), the number of points
designated are used as the destination. Bit devices below the number of points
designated as digits do not change.
Fig 3.6 Ladder Example and Processing Conducted
1. When digit designation processing is conducted, a random value can be used
for the bit device initial device number.
2. Digit designation cannot be made for the direct access I/O (DX, DY).
Ladder Example Processing
With 32 bit Instructions
Ladder Example Processing
When source (S) data is a numerical value
When source (S) data is a word device
0 0
X3
b0
D0
K1X0
b1
b2b3
0000000000
X2 X1 X0
Filled with 0s
X3
X2 X1
X0
00
D1
00000000000000
Filled with 0s
b31 b16
b15b4
X10
DMOVK1X0 D0
Source (S) data
10 0 10100
00 1 00 011
1
000
M19
M16
Not changed
1
0 0
1
0
1
00
1
00
11 1
00
10000011
10011 100
3 4
5
6
7
8 1 2
H78123456
K5M0
M15 M8
M7
M0
M31 M20
X10
DMOV H78123456 K5M0
Destination (D)
100 1 1 101
M17
M10
b15 b8
0
b7
01 1 0 1 11
b0
D1
11
0
1
Not changed
100 1 1 101
b7 b0
D0
1001110 0
10000011
1001110 0
b15b8
M25 M18
M41 M30M29M26
X10
DMOV D0 K5M10
Destination (D)