SPI-4.2 Lite v4.3 User Guide www.xilinx.com 67
UG181 June 27, 2008
Sink Core
R
Insertion of DIP2 Errors
The sink core enables you to force the insertion of DIP2 errors for use during system testing
and debugging. This is supported by the SnkDIP2ErrRequest signal. When the
SnkDIP2ErrRequest signal is asserted, the next DIP2 value is sent on RStat is erred.
The erroneous DIP2 value is an inversion of the correctly calculated DIP2.
Sink Static Configuration Signals
The sink static configuration signals are inputs to the core that are statically driven to
determine the behavior of the core. See Table 2-6, page 27 for a full list of static
configuration signals.
Two of the Sink Static Configuration signals can be changed in circuit. There are static
registers for SnkCalendar_M and SnkCalendar_Len that are synchronous to
SnkStatClk. To change these parameters while the core is operational, first deassert
SnkEn.
FifoAFMode and Sink Almost Full
You can select the behavior of the Sink core when it is almost full. This is done by setting
the static configuration signal Sink FIFO in Almost Full Mode (FifoAFMode[1:0]).
Figure 4-14, Figure 4-15, and Figure 4-16 are timing diagrams illustrating the behavior of
the core for each of the three modes.
FIFO Almost Full Mode “00”
When the FIFO Almost Full Mode (FifoAFMode) is set to “00” and the Sink core becomes
Almost Full, the Sink interface will go out-of-frame, and the Sink Status logic sends the
framing sequence “11” until SnkAlmostFull_n is deasserted, and the Sink core
transitions back to in-frame. This is illustrated in Figure 4-12.
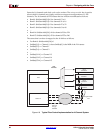
Figure 4-11: Sink Status Path - User Interface to SPI-4.2 Interface
SnkCalendar_M
SnkCalendar_Len
SnkStatClk
SnkStat[31:0]
0x00000002 0x000000A2
SnkStatAddr[3:0] 0000
SnkStatMask[15:0]
SnkStatWr_n
0000.0000.0000.1111
0x000000AA
0 = 0000 0000
3 = 0 0000 0011
RSClk
RStat
0011 10 11 10 10 11 10
DIP
00
DIP DIP
11