E6581301
F-31
6
■ Torque bias function
Using this function, the load can be started
smoothly, by the motor produces enough torque
for load portion before the brake is released,
[Selection of external signals]
6.18 Acceleration/deceleration suspend function
H
HH
H :
Acceleration/deceleration
suspend function
H
HH
H :
Acceleration suspend frequency
H
HH
H : Acceleration suspend time
H
HH
H :
Deceleration suspend frequency
H
HH
H : Deceleration suspend time
• Function
Using these parameters, acceleration or deceleration can be suspended to let the motor run at a constant
speed. There are two ways to suspend acceleration or deceleration: suspending it automatically by setting
the suspend frequency and time using parameters, and suspending it by means of a signal from an
external control device.
These parameters are useful in starting and stopping transfer equipment, textile machines (winders), and
so on.
[Parameter setting]
Title Function Adjustment range Setting value
H Acceleration/deceleration suspend function
:Disabled
:Parameter setting
:Terminal input
H Acceleration suspend frequency ~HJ Hz
H Acceleration suspend time ~ sec.
H Deceleration suspend frequency ~HJ Hz
H Deceleration suspend time ~ sec.
Note1: The acceleration suspend frequency (H) should not be set below the starting frequency (H).
Note2: The deceleration suspend frequency (H) should not be set below the stop frequency (H).
Note3: If the output frequency is lowered by a stall prevention function, the acceleration suspend function may be
activated.
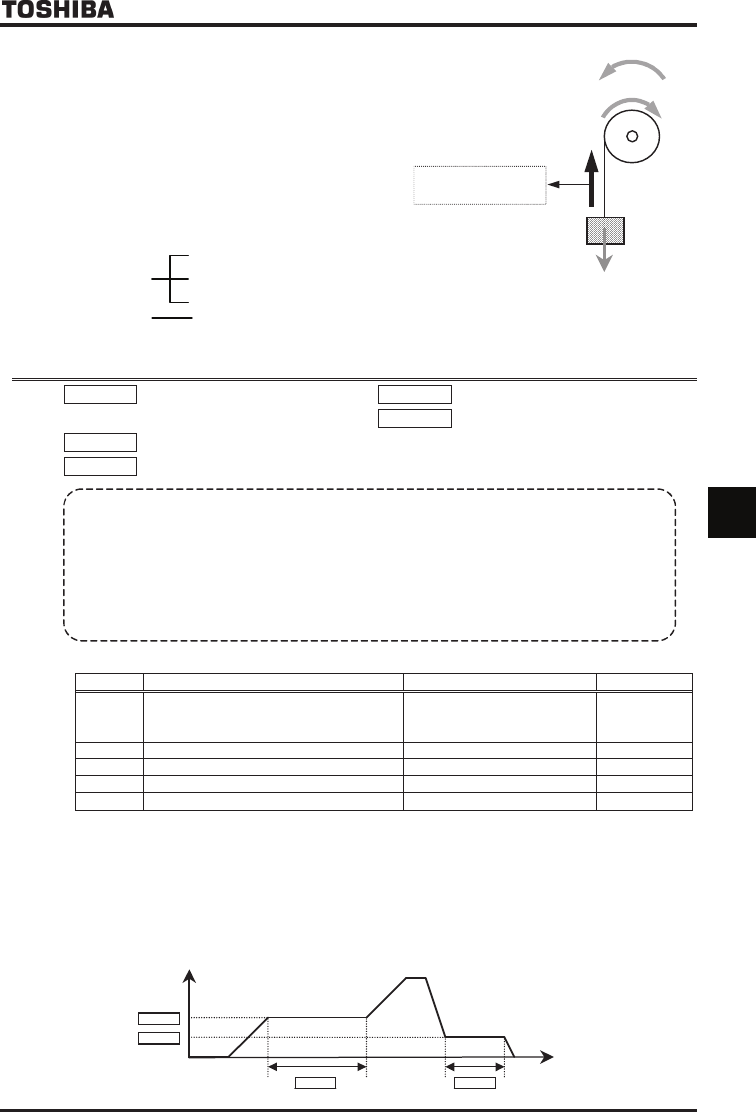
1) To suspend acceleration or deceleration automatically
Set the desired frequency with H or H and the desired time with H or H, and then set
H to .
When the frequency set is reached, the motor stops accelerating or decelerating to rotate at a constant speed.
Output frequency [Hz]
H
Time [s]
H
H
H
H
RR/S4-CCA – 0~10V (0~250%)
RX-CCA – 0~±10V (-250~250%)
VI/II-CCA – 0~10V (0~250%)
VI/II-CCA – 4(0)~20mA (0~250%)
Voltage signals
Current signals
Additional torque
(fixed direction)
Reverse run
Forward run
Tension torque bias
as additional torque