E6581301
E-25
5
3) Inverter overload characteristics
Set to protect the inverter unit. Cannot be turned off by parameter setting.
The inverter has two overload detecting functions, which can be switched from one to another using parameter
H (temperature detection).
[Parameter setting]
Title Function Adjustment range Default setting
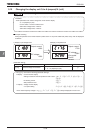
H Temperature detection
:Standard (150%-60 sec.)
: Estimation of temperature
If the inverter overload trip function (QN) is activated frequently, this can be improved by adjusting the stall
operation level H downward or increasing the acceleration time CEE or deceleration time FGE.
■
■■
■ H= (Standard)
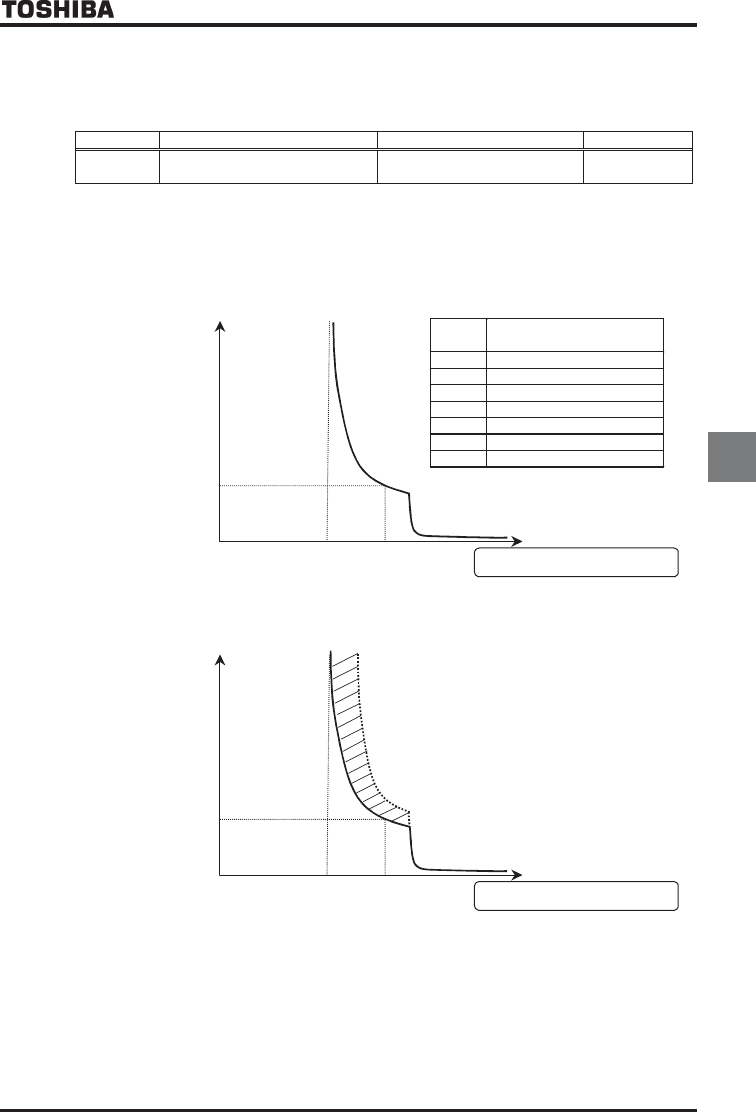
Protection is given uniformly regardless of ambient temperature, as shown by the 150%-60 sec overload curve in
the figure below.
60
100%: Inverter rated output
current
time
[s]
Inverter overload
Monitored output current [%]
0
110%
150%
Current
[%]
Inverter overload time [s]
(Outline data)
111 2400
120 240
130 120
140 80
150 60
165 2
200 0.1
Inverter overload protection characteristics
■
■■
■ H= (Estimation of temperature)
This parameter adjusts automatically overload protection, predicting the inverter internal temperature rise.
(diagonally shaded area in the figure below)
60
100%: Inverter rated output current
time
[s]
Monitored output current [%]
0
110%
150%
Inverter overload protection characteristics
Note 1: If the load applied to the inverter exceeds 150% of its rated load or the operation frequency is less than
0.1Hz, the inverter may trip (QN or QER~QER) in a shorter time.
Note 2: The inverter is factory-set so that, if the inverter becomes overloaded, it will automatically reduce the
carrier frequency to avoid an overload trip (QN or QER~QER). A reduction in carrier frequency
causes an increase in noise from the motor, but this does not affect the performance of the inverter.
If you do not want the inverter to reduce the carrier frequency automatically, set the parameter
H=.
Note 3: Overload detection level is variable by condition of output frequency and carrier frequency.