Using GPIB, RS-232
GB1400 User Manual D-3
query command. The GB1400 responses commands will be either character
mnemonics (for example, INT or EXT) or numerics (Example: 200.0).
GPIB Numeric Responses
When responding with a numeric, the receiver specifies it as one of the following
types:
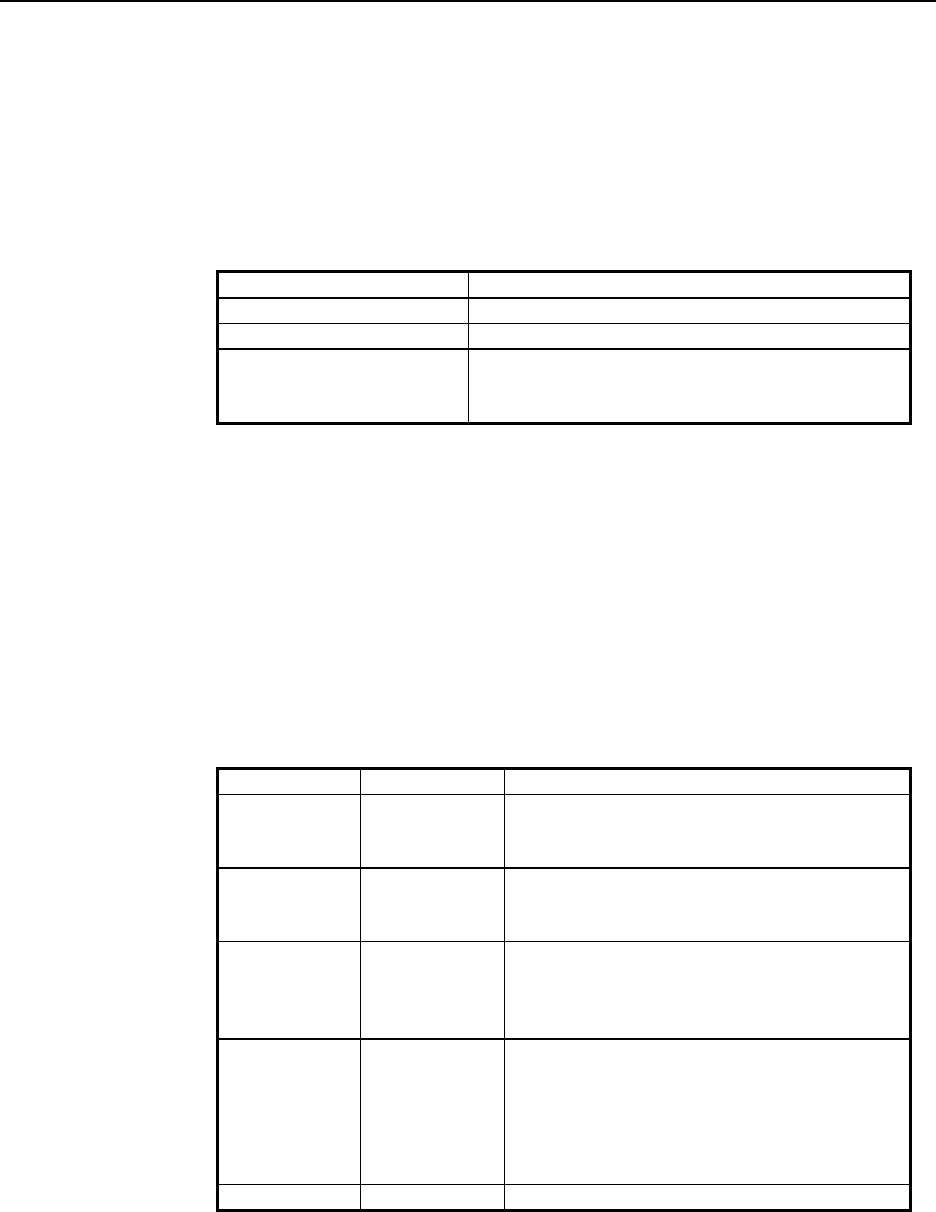
<NR1 Numeric>: decimal integer
<NR2 Numeric>: decimal real number without exponent
<NR3 Numeric>: decimal real number with exponent
<Non-decimal Numeric>: non-decimal number with leading #H (Hex), #Q
(Octal), #B (Binary) and always in the range of 0
to 255 decimal (for example, #H55)
GPIB Status Reporting
There is a status reporting function provided for the GPIB interface, which is
based on the SRQ (Service Request) and is defined in the ANSI/IEEE standard
488.2-1987. The implementation used by GB1400 for status reporting includes one
additional register from what is specified within the IEEE-488.2 standard.
Status Byte
There is a status byte which is used to define the SRQ status. The individual bits
within the status byte represent the different conditions which might cause the
request for service defined as follows:
Bits 1 to 3 Unused
Bit 4 (TSB) Test
Event Status
Bit
This is a summary of Test Event Status
Byte. It will be set whenever an enabled
Test event condition occurs
Bit 5 (MAV)
Message
Available Bit
Set whenever there is output available for
the controller
Bit 6 (ESB)
Standard
Event Status
Bit
This is the summary of the Standard Event
Status Byte. It will be set whenever an
enabled standard event condition occurs
Bit 7 (MSS) Master
Summary
Status Bit
This is the Master Summary Status. It is a
summary of the status byte, so that
whenever one of the bits (TSB, MAV or
ESB) is set and it is also enabled (by the
Service Request Enable byte), the MSS bit
will set
Bit 8 Unused


















