F-75
Broadcast communications
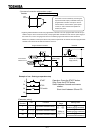
When the host computer to inverters broadcasts an operation frequency reference.
The host computer transmits data to inverters.
Each inverter receives data from the host computer and checks the number specified by the
computer against its number.
If an asterisk ( ) is marked in place of an inverter number, all inverters judge the data to be common
to them (broadcast message), decode the command and take action.
To avoid collision between data sets, data from the inverter with an a zero instead of an asterisk only
is sent back to the host computer.
In this case, all inverters operate, following the operation frequency command given by the host
computer across the network.
Note) Data can also be broadcast to a specific group of inverters (group broadcast communication
s) by putting a number common to each inverter in the group.(This function is usable only in
ASCII mode.)
(Ex.) If " 1" is designated, data is broadcast to all inverters bearing the numbers 01, 11, 21,
31, ... 91, and data from the inverter bearing 01 only is sent back to the host.
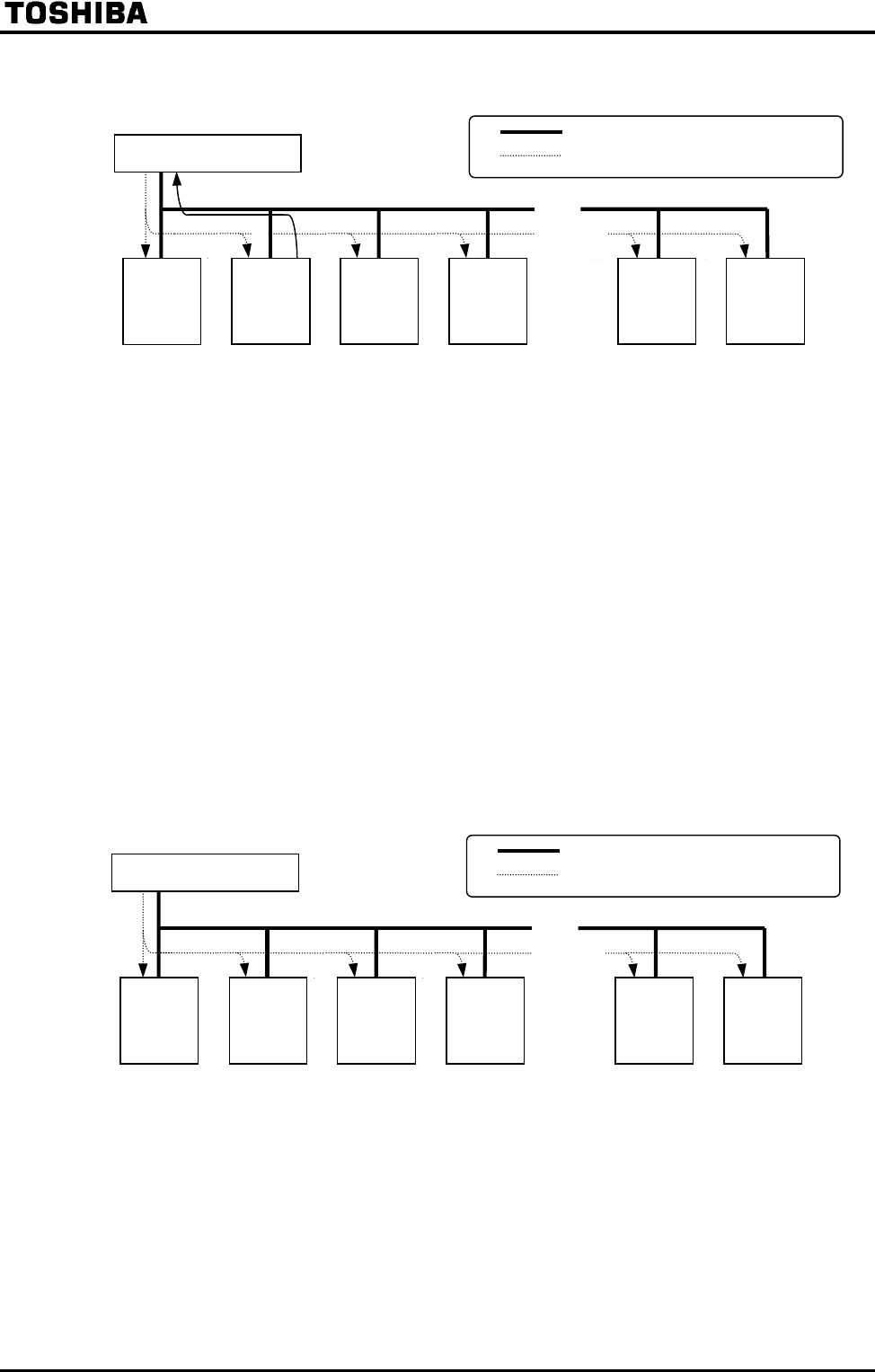
Inter-drive communications
When inverters (slaves) operate at the same operating frequency as the master inverter to which
they are connected (No frequency point is set.)
The master inverter transmits frequency command data to its slave inverters.
The slave inverters calculate a frequency reference from the data received and save the frequency
calculated.
As a result, all slave inverters operate at the same frequency as the master inverter.
(Note) The master inverter always sends frequency command data to its slave inverters, and all slave
inverters are always waiting for frequency command data from the master inverter.
Master inverter
Wiring
Data Master slave
Use a terminal board, etc., to divide each cable into branches.
Use a terminal board, etc., to divide each cable into branches.
Wiring
Data Host Inverter
Host computer