9
1
OUTLINE
Installation of the drive unit and enclosure design
1.4.2 Cooling system types for drive unit panel
From the panel that contains the drive unit, the heat of the drive unit and other equipment (transformers, lamps, resistors, etc.)
and the incoming heat such as direct sunlight must be dissipated to keep the in-panel temperature lower than the permissible
temperatures of the in-panel equipment including the drive unit.
The cooling systems are classified as follows in terms of the cooling calculation method.
1) Cooling by natural heat dissipation from the enclosure surface (totally enclosed type)
2) Cooling by heat sink (aluminum fin, etc.)
3) Cooling by ventilation (forced ventilation type, pipe ventilation type)
4) Cooling by heat exchanger or cooler (heat pipe, cooler, etc.)
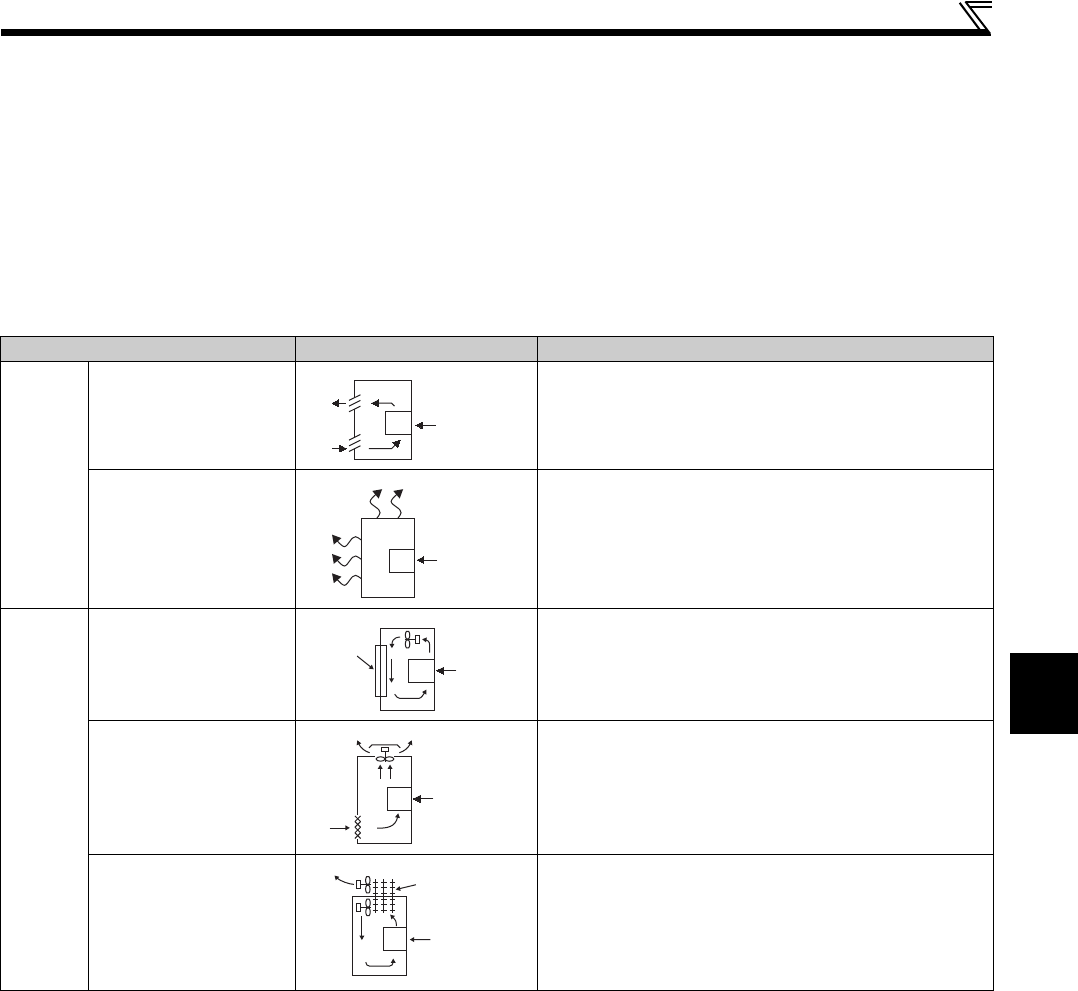
Cooling System Panel Structure Comment
Natural
cooling
Natural ventilation
(enclosed, open type)
Low in cost and generally used, but the panel size increases
as the drive unit capacity increases. For relatively small
capacities.
Natural ventilation
(totally enclosed type)
Being a totally enclosed type, the most appropriate for hostile
environment having dust, dirt, oil mist, etc. The panel size
increases depending on the drive unit capacity.
Forced
cooling
Fin cooling
Having restrictions on the heatsink mounting position and
area, and designed for relative small capacities.
Forced ventilation
For general indoor installation. Appropriate for panel
downsizing and cost reduction, and often used.
Heat pipe Totally enclosed type for panel downsizing.
Drive unit
Drive unit
Drive unit
Heatsink
Drive unit
Drive unit
Heat pipe


















