4. Servo Adjustment
4 - 10
(3) Adjusting the in-position width
Because there is a response delay in the servomotor drive due to position loop control, a "settling
time" is also required for the motor to actually stop after the command speed from the CNC reaches
0.
The movement command in the next block is generally started after it is confirmed that the
machine has entered the "in-position width" range set for the machine.
Set the precision required for the machine as the in-position width. If a high precision is set
needlessly, the cycle time will increase due to a delay in the settling time.
The in-position width is validated with the servo parameter settings, but there may be cases when
it is validated with the NC parameters. Refer to each NC Instruction Manual.
No. Abbrev. Parameter name Explanation Setting range
SV024 INP In-position detection
width
Set the in-position detection width.
Set the accuracy required for the machine.
The lower the setting is, the higher the positioning accuracy gets,
however, the cycle time (setting time) becomes longer. The standard
setting is "50".
0 to 32767
(µm)
POINT
The in-position width setting and confirmation availability depend on the CNC
parameters.
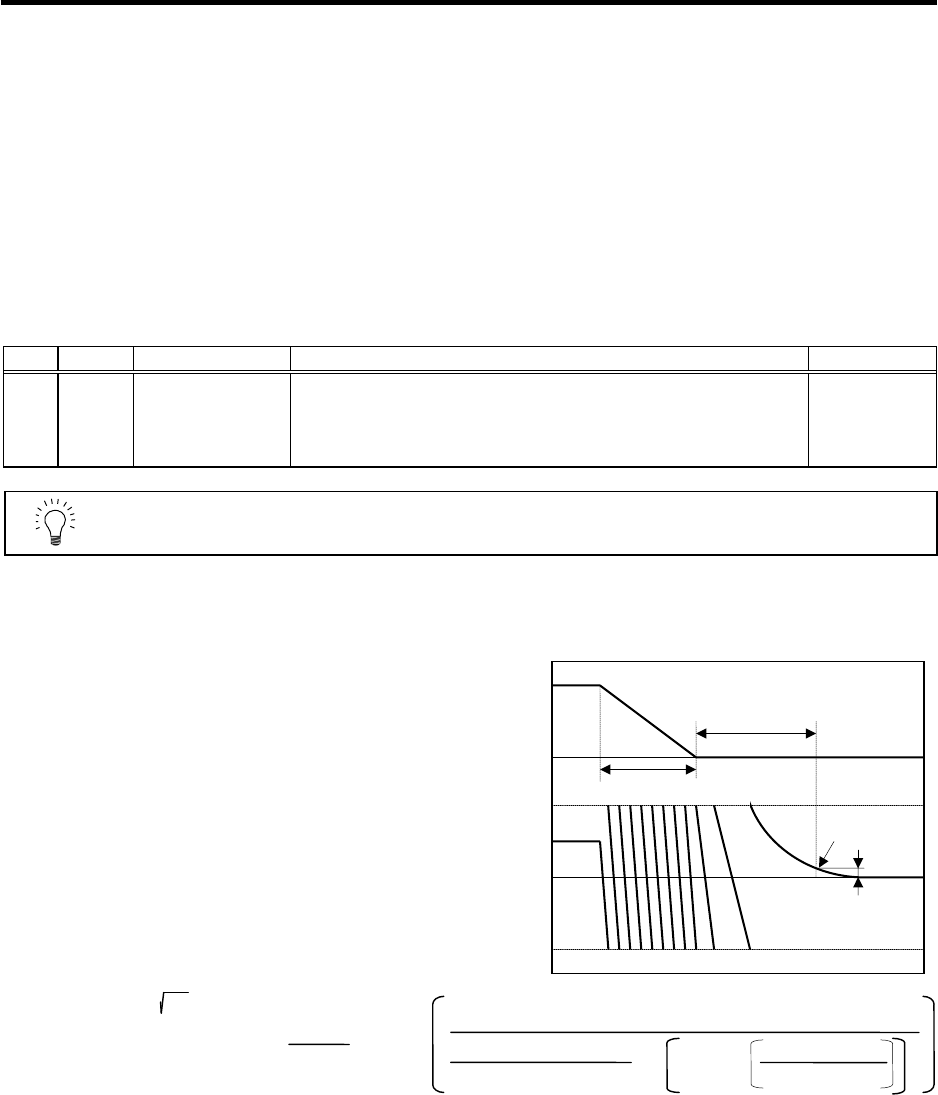
(4) Adjusting the settling time
The settling time is the time required for
the position droop to enter the in-position
width after the feed command (F∆T) from
the CNC reaches 0.
The settling time can be shortened by
raising the position loop gain or using
SHG control. However, a sufficient
response (sufficiently large VGN1 setting)
for the speed loop is required to carry out
stable control.
The settling time during normal control
when the CNC is set to linear acceleration/
deceleration can be calculated using the
following equation. During SHG control,
estimate the settling time by multiplying
PGN1 by
2
.
PGN1 : Position loop gain1 (SV003) (rad/s)
F : Rapid traverse rate (mm/min)
G0tL : Rapid traverse linear acceleration/
deceleration time constant (ms)
INP : In-position width (SV024) (µm)
Settling time (ms) = -
•
PGN1
10
3
INP
F × 10
6
60×G0tL×PGN1
2
×
1- exp
PGN1×G0tL
10
3
ln
0
0
F∆T
Position
droop
F
Time
Setting time
In-position
In-position width
G0tL