Dial Plan Setup Operations
Polycom, Inc. 499
You cannot use least-cost routing when:
• The route cannot be identified.
• The required resources are unavailable.
• Bandwidth limitations exist on the WAN.
How Least-Cost Routing Works
Each LCR table defines dial strings, which include the country code, area code,
prefix, and a weighted cost for commonly made calls. You usually create one
LCR table per site.
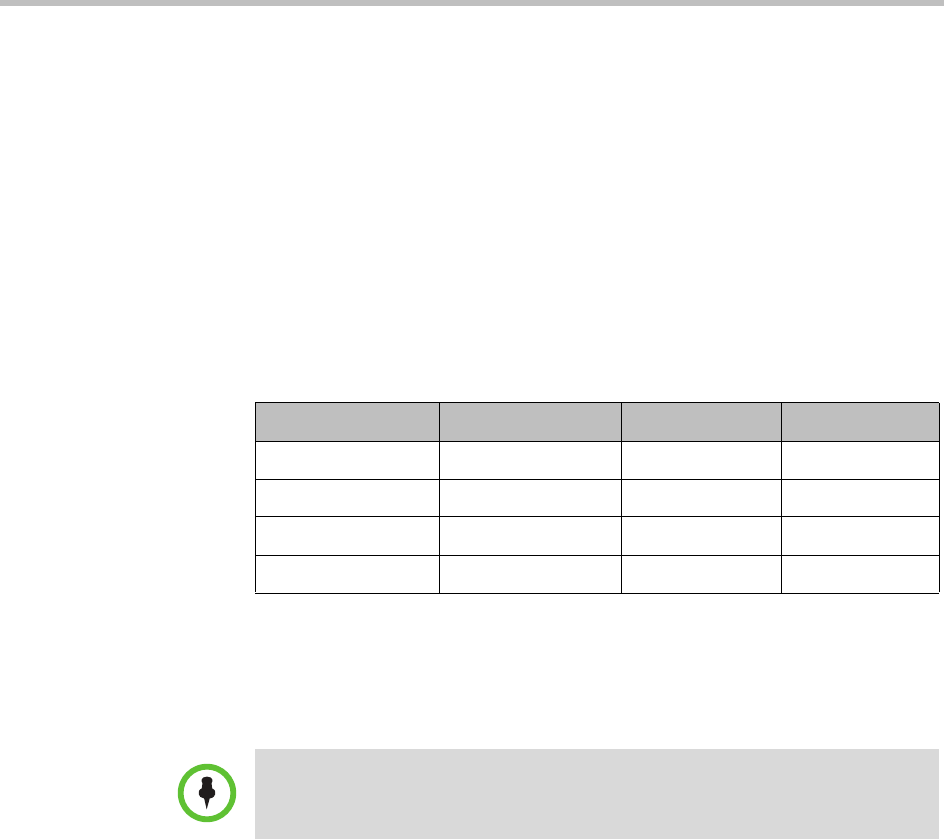
The following table is an example of an LCR table.
The CMA system compares the dial string for a call to the dial strings in LCR
tables. The dial string can match at the country code, area code, or prefix level.
The CMA system reads the “# of digits to strip” field to determine how many
digits to remove.
Before determining the final call routing, the CMA system considers cost
(through LCR tables), bandwidth resources (through site topology and device
group policies), and gateway availability.
Example of Least-Cost Routing
Company ABC has three sites: Site A in San Jose, CA, Site B in Monterey, CA,
and Site C in Washington, D.C. All sites have gateways.
LCR Tables for Three Sites
The LCR tables included area codes that are used frequently in each site and
considered that calls are made frequently from Site C to Southern California.
Country Code Area Code Prefix Weighted Cost
1 408 565 0
1 408 0
1 650 0
1 415 5
Note
For areas of the United States that do not require you dial an access code before
the area code, exclude this number when you define the number of digits to strip.


















